Evaluation of the effect of naproxen on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of apixaban
- PMID: 24697979
- PMCID: PMC4239981
- DOI: 10.1111/bcp.12393
Evaluation of the effect of naproxen on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of apixaban
Abstract
Aim: To assess pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic interactions between naproxen (a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug) and apixaban (an oral, selective, direct factor-Xa inhibitor).
Method: In this randomized, three period, two sequence study, 21 healthy subjects received a single oral dose of apixaban 10 mg, naproxen 500 mg or co-administration of both. Blood samples were collected for determination of apixaban and naproxen pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics (anti-Xa activity, international normalized ratio [INR] and arachidonic acid-induced platelet aggregation [AAI-PA]). Adverse events, bleeding time and routine safety assessments were also evaluated.
Results: Apixaban had no effect on naproxen pharmacokinetics. However, following co-administration, apixaban AUC(0,∞), AUC(0,t) and Cmax were 54% (geometric mean ratio 1.537; 90% confidence interval (CI) 1.394, 1.694), 55% (1.549; 90% CI 1.400, 1.713) and 61% (1.611; 90% CI 1.417, 1.831) higher, respectively. Mean (standard deviation [SD]) anti-Xa activity at 3 h post-dose was approximately 60% higher following co-administration compared with apixaban alone, 4.4 [1.0] vs. 2.7 [0.7] IU ml(-1) , consistent with the apixaban concentration increase following co-administration. INR was within the normal reference range after all treatments. AAI-PA was reduced by approximately 80% with naproxen. Co-administration had no impact beyond that of naproxen. Mean [SD] bleeding time was higher following co-administration (9.1 [4.1] min) compared with either agent alone (5.8 [2.3] and 6.9 [2.6] min for apixaban and naproxen, respectively).
Conclusion: Co-administration of naproxen with apixaban results in higher apixaban exposure and appears to occur through increased apixaban bioavailability. The effects on anti-Xa activity, INR and inhibition of AAI-PA observed in this study were consistent with the individual pharmacologic effects of apixaban and naproxen.
Keywords: P-glycoprotein; anticoagulant; apixaban; clinical pharmacology; factor Xa; naproxen drug interaction.
© 2014 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures
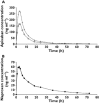
 , apixaban alone;
, apixaban alone;  , co-administration of apixaban and naproxen;
, co-administration of apixaban and naproxen;  , naproxen alone;
, naproxen alone;  , co-administration of apixaban and naproxen
, co-administration of apixaban and naproxen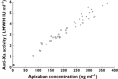
 , naproxen alone;
, naproxen alone;  , co-administration of apixaban and naproxen
, co-administration of apixaban and naproxenReferences
-
- Lassen MR, Raskob GE, Gallus A, Pineo G, Chen D, Portman RJ. Apixaban or enoxaparin for thromboprophylaxis after knee replacement. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:594–604. - PubMed
-
- Lassen MR, Raskob GE, Gallus A, Pineo G, Chen D, Hornick P. Apixaban versus enoxaparin for thromboprophylaxis after knee replacement (ADVANCE-2): a randomised double-blind trial. Lancet. 2010;375:807–815. - PubMed
-
- Lassen MR, Gallus A, Raskob GE, Pineo G, Chen D, Ramirez LM. Apixaban versus enoxaparin for thromboprophylaxis after hip replacement. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:2487–2498. - PubMed
-
- Connolly SJ, Eikelboom J, Joyner C, Diener HC, Hart R, Golitsyn S, Flaker G, Avezum A, Hohnloser SH, Diaz R, Talajic M, Zhu J, Pais P, Budaj A, Parkhomenko A, Jansky P, Commerford P, Tan RS, Sim KH, Lewis BS, Van Mieghem W, Lip GY, Kim JH, Lanas-Zanetti F, Gonzalez-Hermosillo A, Dans AL, Munawar M, O'Donnell M, Lawrence J, Lewis G, Afzal R, Yusuf S. Apixaban in patients with atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 2011;364:806–817. - PubMed
-
- Granger CB, Alexander JH, McMurray JJ, Lopes RD, Hylek E, Hanna M, Al-Khalidi HR, Ansell J, Atar D, Avezum A, Bahit MC, Diaz R, Easton JD, Ezekowitz JA, Flaker G, Garcia D, Geraldes M, Gersh BJ, Golitsyn S, Goto S, Hermosillo AG, Hohnloser S, Horowitz J, Mohan P, Jansky P, Lewis BS, Lopez-Sendon J, Pais P, Parkhomenko A, Verheugt F, Zhu J, Wallentin L. Apixaban versus warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:981–992. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

