Subjective cognitive concerns and neuropsychiatric predictors of progression to the early clinical stages of Alzheimer disease
- PMID: 24698445
- PMCID: PMC4145054
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jagp.2014.02.007
Subjective cognitive concerns and neuropsychiatric predictors of progression to the early clinical stages of Alzheimer disease
Abstract
Objective: To examine neuropsychiatric and neuropsychological predictors of progression from normal to early clinical stages of Alzheimer disease (AD).
Methods: From a total sample of 559 older adults from the Massachusetts Alzheimer's Disease Research Center longitudinal cohort, 454 were included in the primary analysis: 283 with clinically normal cognition (CN), 115 with mild cognitive impairment (MCI), and 56 with subjective cognitive concerns (SCC) but no objective impairment, a proposed transitional group between CN and MCI. Two latent cognitive factors (memory-semantic, attention-executive) and two neuropsychiatric factors (affective, psychotic) were derived from the Alzheimer's Disease Centers' Uniform Data Set neuropsychological battery and Neuropsychiatric Inventory brief questionnaire. Factors were analyzed as predictors of time to progression to a worse diagnosis using a Cox proportional hazards regression model with backward elimination. Covariates included baseline diagnosis, gender, age, education, prior depression, antidepressant medication, symptom duration, and interaction terms.
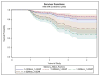
Results: Higher/better memory-semantic factor score predicted lower hazard of progression (hazard ratio [HR] = 0.4 for 1 standard deviation [SD] increase, p <0.0001), and higher/worse affective factor score predicted higher hazard (HR = 1.3 for one SD increase, p = 0.01). No other predictors were significant in adjusted analyses. Using diagnosis as a sole predictor of transition to MCI, the SCC diagnosis carried a fourfold risk of progression compared with CN (HR = 4.1, p <0.0001).
Conclusion: These results identify affective and memory-semantic factors as significant predictors of more rapid progression from normal to early stages of cognitive decline and highlight the subgroup of cognitively normal elderly with SCC as those with elevated risk of progression to MCI.
Keywords: Alzheimer disease; Neuropsychiatric and neuropsychological factors; mild cognitive impairment; subjective cognitive concerns.
Copyright © 2014 American Association for Geriatric Psychiatry. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
No disclosures to report.
Figures
References
-
- Reisberg B, Gauthier S. Current evidence for subjective cognitive impairment (SCI) as the pre-mild cognitive impairment (MCI) stage of subsequently manifest Alzheimer’s disease. Int Psychogeriatr. 2008;20(1):1–16. - PubMed
-
- Storandt M, Grant EA, Miller JP, et al. Longitudinal course and neuropathologic outcomes in original vs revised MCI and in pre-MCI. Neurology. 2006;67(3):467–73. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

