Regulation of mTORC1 by amino acids
- PMID: 24698685
- PMCID: PMC4074565
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tcb.2014.03.003
Regulation of mTORC1 by amino acids
Abstract
The mechanistic target of rapamycin complex I (mTORC1) is a central regulator of cellular and organismal growth, and hyperactivation of this pathway is implicated in the pathogenesis of many human diseases including cancer and diabetes. mTORC1 promotes growth in response to the availability of nutrients, such as amino acids, which drive mTORC1 to the lysosomal surface, its site of activation. How amino acid levels are communicated to mTORC1 is only recently coming to light by the discovery of a lysosome-based signaling system composed of Rags (Ras-related GTPases) and Ragulator v-ATPase, GATOR (GAP activity towards Rags), and folliculin (FLCN) complexes. Increased understanding of this pathway will not only provide insight into growth control but also into the human pathologies triggered by its deregulation.
Keywords: GATOR complex; Rag GTPases; Ragulator; amino acid sensing; folliculin.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
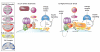
References
-
- Hsu PP, Kang SA, Rameseder J, Zhang Y, Ottina KA, Lim D, Peterson TR, Choi Y, Gray NS, Yaffe MB, Marto JA, Sabatini DM. The mTOR-regulated phosphoproteome reveals a mechanism of mTORC1-mediated inhibition of growth factor signaling. Science. 2011;332:1317–1322. published online EpubJun 10 (10.1126/science.1199498) - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yu Y, Yoon SO, Poulogiannis G, Yang Q, Ma XM, Villen J, Kubica N, Hoffman GR, Cantley LC, Gygi SP, Blenis J. Phosphoproteomic analysis identifies Grb10 as an mTORC1 substrate that negatively regulates insulin signaling. Science. 2011;332:1322–1326. published online EpubJun 10 (10.1126/science.1199484) - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kim DH, Sarbassov DD, Ali SM, King JE, Latek RR, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Sabatini DM. mTOR interacts with raptor to form a nutrient-sensitive complex that signals to the cell growth machinery. Cell. 2002;110:163–175. published online EpubJul 26 ( - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

