Arabidopsis florigen FT binds to diurnally oscillating phospholipids that accelerate flowering
- PMID: 24698997
- PMCID: PMC3988816
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms4553
Arabidopsis florigen FT binds to diurnally oscillating phospholipids that accelerate flowering
Abstract
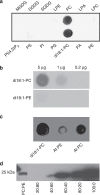
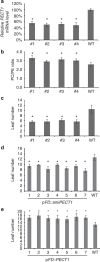
Arabidopsis FT protein is a component of florigen, which transmits photoperiodic flowering signals from leaf companion cells to the shoot apex. Here, we show that FT specifically binds phosphatidylcholine (PC) in vitro. A transgenic approach to increase PC levels in vivo in the shoot meristem accelerates flowering whereas reduced PC levels delay flowering, demonstrating that PC levels are correlated with flowering time. The early flowering is related to FT activity, because expression of FT-effector genes is increased in these plants. Simultaneous increase of FT and PC in the shoot apical meristem further stimulates flowering, whereas a loss of FT function leads to an attenuation of the effect of increased PC. Specific molecular species of PC oscillate diurnally, and night-dominant species are not the preferred ligands of FT. Elevating night-dominant species during the day delays flowering. We suggest that FT binds to diurnally changing molecular species of PC to promote flowering.
Figures


References
-
- Andrés F. & Coupland G. The genetic basis of flowering responses to seasonal cues. Nat. Rev. Genet. 13, 627–639 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Corbesier L. et al. FT protein movement contributes to long-distance signaling in floral induction of Arabidopsis. Science 316, 1030–1033 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Tamaki S., Matsuo S., Wong H. L., Yokoi S. & Shimamoto K. Hd3a protein is a mobile flowering signal in rice. Science 316, 1033–1036 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Mathieu J., Warthmann N., Küttner F. & Schmid M. Export of FT protein from phloem companion cells is sufficient for floral induction in Arabidopsis. Curr. Biol. 17, 1055–1060 (2007). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

