Ribavirin improves the IFN-γ response of natural killer cells to IFN-based therapy of hepatitis C virus infection
- PMID: 24700342
- PMCID: PMC4469648
- DOI: 10.1002/hep.27092
Ribavirin improves the IFN-γ response of natural killer cells to IFN-based therapy of hepatitis C virus infection
Abstract
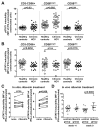
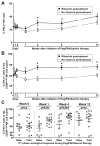
Ribavirin (RBV) is an important component of interferon (IFN)-based and direct antiviral treatment regimens for hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection. Immunomodulation, in particular improvement of the host IFN response, has been proposed as RBV's mechanism of action. Natural killer (NK) cells are sensitive biomarkers for IFN-α/β receptor signaling, as NK cell cytotoxicity and IFN-γ production are regulated by signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT)1- and STAT4-phosphorylation, respectively. Specifically, pSTAT1-dependent NK cell cytotoxicity increases and pSTAT4-dependent IFN-γ production decreases in response to endogenous, virus-induced IFN-α and during IFN-α-based therapy. To assess whether RBV has a direct effect on NK cells and/or improves the IFN-γ response of NK cells in the presence of IFN-α, we prospectively studied 22 HCV patients with and 32 patients without 4 weeks of RBV pretreatment, who all received subsequent pegylated (Peg)IFN/ribavirin combination therapy. During RBV pretreatment, both the frequency of CD56(dim) NK cells with cytotoxic effector functions and the frequency of CD56(bright) NK cells with the capacity to produce IFN-γ decreased (P = 0.049 and P = 0.001, respectively). In vitro or in vivo exposure of NK cells to RBV improved the pSTAT4 (P < 0.01) but not pSTAT1 response of NK cells to subsequent stimulation with IFN-α. This was associated with an increase in IFN-γ production but not cytotoxicity of NK cells during subsequent IFN-α-based therapy. The frequency of IFN-γ-producing NK cells was greater in fast second-phase virological responders than in slow responders.
Conclusion: RBV enhances the pSTAT4 and IFN-γ response of NK cells to IFN-α-stimulation.
Published 2014. This article is a U.S. Government work and is in the public domain in the USA.
Figures



Comment in
-
The multifaceted functions of ribavirin: antiviral, immunomodulator, or both?Hepatology. 2014 Oct;60(4):1126-9. doi: 10.1002/hep.27186. Epub 2014 Jun 26. Hepatology. 2014. PMID: 24753082 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Early changes in interferon signaling define natural killer cell response and refractoriness to interferon-based therapy of hepatitis C patients.Hepatology. 2012 Jan;55(1):39-48. doi: 10.1002/hep.24628. Epub 2011 Nov 14. Hepatology. 2012. PMID: 21898483 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
PEG-IFN alpha but not ribavirin alters NK cell phenotype and function in patients with chronic hepatitis C.PLoS One. 2014 Apr 21;9(4):e94512. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0094512. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24751903 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Rapid decrease in hepatitis C viremia by direct acting antivirals improves the natural killer cell response to IFNα.Gut. 2017 Apr;66(4):724-735. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2015-310033. Epub 2016 Jan 4. Gut. 2017. PMID: 26733671 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of hepatitis C virus genotype 3-infection.Liver Int. 2014 Feb;34 Suppl 1:18-23. doi: 10.1111/liv.12405. Liver Int. 2014. PMID: 24373074 Review.
-
Consensus guidelines for the management of hepatitis C infection.Saudi Med J. 2003 Jul;24 Suppl 2:S99-118. Saudi Med J. 2003. PMID: 25121186
Cited by
-
Type I Interferon Elevates Co-Regulatory Receptor Expression on CMV- and EBV-Specific CD8 T Cells in Chronic Hepatitis C.Front Immunol. 2015 Jun 10;6:270. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00270. eCollection 2015. Front Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26113847 Free PMC article.
-
Randomized Trial Evaluating the Impact of Ribavirin Mono-Therapy and Double Dosing on Viral Kinetics, Ribavirin Pharmacokinetics and Anemia in Hepatitis C Virus Genotype 1 Infection.PLoS One. 2016 May 11;11(5):e0155142. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0155142. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27167219 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Bracing NK cell based therapy to relegate pulmonary inflammation in COVID-19.Heliyon. 2021 Jul;7(7):e07635. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e07635. Epub 2021 Jul 21. Heliyon. 2021. PMID: 34312598 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Achieving sustained virologic response after interferon-free hepatitis C virus treatment correlates with hepatic interferon gene expression changes independent of cirrhosis.J Viral Hepat. 2016 Jul;23(7):496-505. doi: 10.1111/jvh.12510. Epub 2016 Feb 3. J Viral Hepat. 2016. PMID: 26840694 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The Dual Nature of Type I and Type II Interferons.Front Immunol. 2018 Sep 11;9:2061. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02061. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30254639 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pawlotsky JM, Dahari H, Neumann AU, Hezode C, Germanidis G, Lonjon I, Castera L, et al. Antiviral action of ribavirin in chronic hepatitis C. Gastroenterology. 2004;126:703–714. - PubMed
-
- Fried MW, Shiffman ML, Reddy KR, Smith C, Marinos G, Goncales FL, Jr, Haussinger D, et al. Peginterferon alfa-2a plus ribavirin for chronic hepatitis C virus infection. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:975–982. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
