HIV/AIDS epidemic among older adults in China during 2005-2012: results from trend and spatial analysis
- PMID: 24700658
- PMCID: PMC4990827
- DOI: 10.1093/cid/ciu214
HIV/AIDS epidemic among older adults in China during 2005-2012: results from trend and spatial analysis
Abstract
Background: Recent studies have indicated an increasing burden of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)/AIDS among older adults.
Methods: All identified people living with HIV/AIDS (PLWHA) recorded through the Chinese HIV/AIDS CRS during 2005-2012 were included in the study, except for the cases that lacked specific spatial information. Trend tests and spatial analyses were conducted.
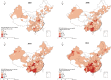
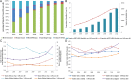
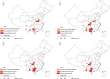
Results: Information about 73,521 PLWHA (aged ≥50 years) was collected during 2005-2012. Three provinces-Guangxi, Henan, and Yunnan-accounted for 54.4% of the identified cases during the study period. Compared with 2005, the ratio between residents and migrants among the study population decreased to 40.1% in 2012. The ratio of HIV-infected patients to AIDS patients and the ratio of males to females increased gradually among older infected adults. Results of spatial analysis indicate a clustered distribution of HIV/AIDS among older adults throughout the country. Hot spots were observed in 4 provinces (Guangxi, Henan, Yunnan, and Sichuan) and 1 municipality (Chongqing). A trend from central provinces toward southern provinces was also identified.
Conclusions: The number and proportion of HIV/AIDS among older adults have increased in recent years. The hot spots showed movement from central to southern China. A focused intervention strategy targeting the older PLWHA is urgently required in China.
Keywords: HIV/AIDS; older adult; spatial analysis.
© The Author 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Infectious Diseases Society of America. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The HIV/AIDS epidemic among young people in China between 2005 and 2012: results of a spatial temporal analysis.HIV Med. 2017 Mar;18(3):141-150. doi: 10.1111/hiv.12408. Epub 2016 Aug 24. HIV Med. 2017. PMID: 27552922 Free PMC article.
-
[Spatial-temporal distribution of newly detected HIV/AIDS cases among aged 15 years or older women in China, 2010-2016].Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2018 Jun 10;39(6):739-744. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2018.06.009. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 29936739 Chinese.
-
Epidemiological and spatiotemporal analyses of HIV/AIDS prevalence among older adults in Sichuan, China between 2008 and 2019: A population-based study.Int J Infect Dis. 2021 Apr;105:769-775. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2021.02.077. Epub 2021 Feb 19. Int J Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 33618006
-
Characteristics of the HIV/AIDS Epidemic in Women Aged 15-49 Years from 2005 to 2012 in China.Biomed Environ Sci. 2015 Oct;28(10):701-8. doi: 10.3967/bes2015.100. Biomed Environ Sci. 2015. PMID: 26582092
-
Prevalence of HIV infection among Chinese voluntary blood donors during 2010-2017: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis.Transfusion. 2019 Nov;59(11):3431-3441. doi: 10.1111/trf.15515. Epub 2019 Sep 18. Transfusion. 2019. PMID: 31532001
Cited by
-
HIV Epidemiology and Prevention in Southwestern China: Trends from 1996-2017.Curr HIV Res. 2019;17(2):85-93. doi: 10.2174/1570162X17666190703163838. Curr HIV Res. 2019. PMID: 31269884 Free PMC article. Review.
-
90-90-90 cascade analysis on reported CLHIV infected by mother-to-child transmission in Guangxi, China: a modeling study.Sci Rep. 2020 Mar 24;10(1):5295. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-62281-8. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32210333 Free PMC article.
-
Disproportionate Increase of New Diagnosis of HIV/AIDS Infection by Sex and Age - China, 2007-2018.China CDC Wkly. 2020 Jan 31;2(5):69-74. China CDC Wkly. 2020. PMID: 34594810 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of and factors associated with advanced HIV disease among newly diagnosed people living with HIV in Guangdong Province, China.J Int AIDS Soc. 2020 Nov;23(11):e25642. doi: 10.1002/jia2.25642. J Int AIDS Soc. 2020. PMID: 33225623 Free PMC article.
-
The HIV/AIDS epidemic among young people in China between 2005 and 2012: results of a spatial temporal analysis.HIV Med. 2017 Mar;18(3):141-150. doi: 10.1111/hiv.12408. Epub 2016 Aug 24. HIV Med. 2017. PMID: 27552922 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chin J. Current and future dimensions of the HIV/AIDS pandemic in women and children. Lancet. 1990;336:221–4. - PubMed
-
- Smith G. Aging hearing: HIV over fifty, exploring the new threat. Washington, DC: Senate Committee on Aging; 2006.
-
- Longo B, Camoni L, Boros S, Suligoi B. Increasing proportion of AIDS diagnoses among older adults in Italy. AIDS Patient Care and STDs. 2008;22:365–71. - PubMed
-
- Program and Policy Implication Prb. HIV/AIDS and older adults in the United States. USA: Today's Research on Aging; 2009.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

