Inorganic phosphate induces cancer cell mediated angiogenesis dependent on forkhead box protein C2 (FOXC2) regulated osteopontin expression
- PMID: 24700685
- PMCID: PMC4183733
- DOI: 10.1002/mc.22153
Inorganic phosphate induces cancer cell mediated angiogenesis dependent on forkhead box protein C2 (FOXC2) regulated osteopontin expression
Abstract
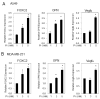
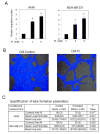
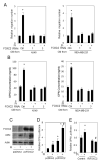
Recent studies in both rodents and humans suggest that elevated serum phosphorus, in the context of normal renal function, potentiates, or exacerbates pathologies associates with cardiovascular disease, bone metabolism, and cancer. Our recent microarray studies identified the potent stimulation of pro-angiogenic genes such as forkhead box protein C2 (FOXC2), osteopontin, and Vegfα, among others in response to elevated inorganic phosphate (Pi). Increased angiogenesis and neovascularization are important events in tumor growth and the progression to malignancy and FOXC2 has recently been identified as a potential transcriptional regulator of these processes. In this study we addressed the possibility that a high Pi environment would increase the angiogenic potential of cancer cells through a mechanism requiring FOXC2. Our studies utilized lung and breast cancer cell lines in combination with the human umbilical vascular endothelial cell (HUVEC) vessel formation model to better understand the mechanism(s) by which a high Pi environment might alter cancer progression. Exposure of cancer cells to elevated Pi stimulated expression of FOXC2 and conditioned medium from the Pi-stimulated cancer cells stimulated migration and tube formation in the HUVEC model. Mechanistically, we define the requirement of FOXC2 for Pi-induced osteopontin (OPN) expression and secretion from cancer cells as necessary for the angiogenic response. These studies reveal for the first time that cancer cells grown in a high Pi environment promote migration of endothelial cells and tube formation and in so doing identify a novel potential therapeutic target to reduce tumor progression.
Keywords: FOXC2; angiogenesis; inorganic phosphate; migration; osteopontin.
© 2014 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
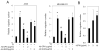
References
-
- Calvo MS. Dietary phosphorus, calcium metabolism and bone. The Journal of nutrition. 1993;123(9):1627–1633. - PubMed
-
- Kemi VE, Karkkainen MU, Karp HJ, Laitinen KA, Lamberg-Allardt CJ. Increased calcium intake does not completely counteract the effects of increased phosphorus intake on bone: an acute dose-response study in healthy females. The British journal of nutrition. 2008;99(4):832–839. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

