Rare bone diseases and their dental, oral, and craniofacial manifestations
- PMID: 24700690
- PMCID: PMC4107543
- DOI: 10.1177/0022034514529150
Rare bone diseases and their dental, oral, and craniofacial manifestations
Abstract
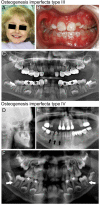
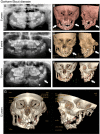
Hereditary diseases affecting the skeleton are heterogeneous in etiology and severity. Though many of these conditions are individually rare, the total number of people affected is great. These disorders often include dental-oral-craniofacial (DOC) manifestations, but the combination of the rarity and lack of in-depth reporting often limit our understanding and ability to diagnose and treat affected individuals. In this review, we focus on dental, oral, and craniofacial manifestations of rare bone diseases. Discussed are defects in 4 key physiologic processes in bone/tooth formation that serve as models for the understanding of other diseases in the skeleton and DOC complex: progenitor cell differentiation (fibrous dysplasia), extracellular matrix production (osteogenesis imperfecta), mineralization (familial tumoral calcinosis/hyperostosis hyperphosphatemia syndrome, hypophosphatemic rickets, and hypophosphatasia), and bone resorption (Gorham-Stout disease). For each condition, we highlight causative mutations (when known), etiopathology in the skeleton and DOC complex, and treatments. By understanding how these 4 foci are subverted to cause disease, we aim to improve the identification of genetic, molecular, and/or biologic causes, diagnoses, and treatment of these and other rare bone conditions that may share underlying mechanisms of disease.
Keywords: Gorham-Stout disease; familial hypophosphatemic rickets; fibrous dysplasia of bone; hyperphosphatemic familial tumoral calcinosis; hypophosphatasia; osteogenesis imperfecta.
© International & American Associations for Dental Research.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the authorship and/or publication of this article.
Figures



References
-
- Akintoye SO, Lee JS, Feimster T, Booher S, Brahim J, Kingman A, et al. (2003). Dental characteristics of fibrous dysplasia and McCune-Albright syndrome. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 96:275-282. - PubMed
-
- Al-Jamali J, Glaum R, Kassem A, Voss PJ, Schmelzeisen R, Schon R. (2012). Gorham-Stout syndrome of the facial bones: a review of pathogenesis and treatment modalities and report of a case with a rare cutaneous manifestations [sic]. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol 114:e23-e29. - PubMed
-
- Benet-Pages A, Orlik P, Strom TM, Lorenz-Depiereux B. (2005). An FGF23 missense mutation causes familial tumoral calcinosis with hyperphosphatemia. Hum Mol Genet 14:385-390. - PubMed
-
- Berdal A, Molla M, Descroix V. (2011). Vitamin D and oral health. In: Vitamin D. Feldman D, Pike JW, Adams JS, editors. San Diego, CA: Academic Press, pp. 521-532.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

