Liposome-encapsulated superoxide dismutase mimetic: theranostic potential of an MR detectable and neuroprotective agent
- PMID: 24700749
- PMCID: PMC3979542
- DOI: 10.1002/cmmi.1559
Liposome-encapsulated superoxide dismutase mimetic: theranostic potential of an MR detectable and neuroprotective agent
Abstract
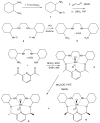
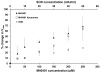
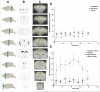
Endogenous manganese based superoxide dismutase (Mn-SOD) provides the primary defense against excess production of potentially toxic superoxide anion (O2 (-) ). M40401 is a synthetic enzyme mimetic that has a catalytic activity rate exceeding that of the native SOD enzymes. The presence of a paramagnetic Mn(II) cation in M40401 suggests that the delivery and spatial distribution of this enzyme mimetic in vivo may be directly detectible using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI); however, the cardiotoxicity of Mn(II) severely limits the use of free M40401 in living systems. To deliver M40401 in vivo in amounts sufficient for MRI detection and to limit potential cardiotoxicity, we encapsulated M40401 into 170 nm liposomes composed of phosphatidylcholine and PEGylated phosphatidylethanolamine to achieve extended circulation in the bloodstream. The obtained liposomes efficiently catalyzed superoxide dismutation in vitro. Using 3 T MRI we investigated the biokinetics of liposome-encapsulated M40401 in mice and found that, in addition to catalyzing superoxide dismutation in vitro, M40401 caused differential and region-specific enhancement of mouse brain after systemic administration. Thus, liposome encapsulated M40401 is an ideal candidate for development as a theranostic compound useful for simultaneous MRI-mediated tracking of delivery as well as for neuroprotective treatment of ischemic brain.
Keywords: M40401; MRI; Mn-SOD; liposomes; manganese complex; mouse brain.
Copyright © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Protective effects of a new stable, highly active SOD mimetic, M40401 in splanchnic artery occlusion and reperfusion.Br J Pharmacol. 2001 Jan;132(1):19-29. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703775. Br J Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11156557 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effect of a new nonpeptidyl mimetic of SOD, M40401, against focal cerebral ischemia in the rat.Brain Res. 2003 Feb 14;963(1-2):8-14. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(02)03796-4. Brain Res. 2003. PMID: 12560107
-
The protective effect of M40401, a superoxide dismutase mimetic, on post-ischemic brain damage in Mongolian gerbils.BMC Pharmacol. 2003 Jun 16;3:8. doi: 10.1186/1471-2210-3-8. Epub 2003 Jun 16. BMC Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 12809567 Free PMC article.
-
An educational overview of the chemistry, biochemistry and therapeutic aspects of Mn porphyrins--From superoxide dismutation to H2O2-driven pathways.Redox Biol. 2015 Aug;5:43-65. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2015.01.017. Epub 2015 Feb 7. Redox Biol. 2015. PMID: 25827425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential Therapeutic Applications of MnSODs and SOD-Mimetics.Chemistry. 2018 Apr 6;24(20):5032-5041. doi: 10.1002/chem.201704561. Epub 2017 Dec 12. Chemistry. 2018. PMID: 29131419 Review.
Cited by
-
Getting into the brain: liposome-based strategies for effective drug delivery across the blood-brain barrier.Int J Nanomedicine. 2016 Oct 18;11:5381-5414. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S117210. eCollection 2016. Int J Nanomedicine. 2016. PMID: 27799765 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrated Proteomics and Lipidomics Investigation of the Mechanism Underlying the Neuroprotective Effect of N-benzylhexadecanamide.Molecules. 2018 Nov 9;23(11):2929. doi: 10.3390/molecules23112929. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 30424008 Free PMC article.
-
Crossing the Blood-Brain Barrier: Advances in Nanoparticle Technology for Drug Delivery in Neuro-Oncology.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 9;23(8):4153. doi: 10.3390/ijms23084153. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35456971 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanotheranostics: The Fabrication of Theranostics with Nanoparticles and their Application to Treat the Neurological Disorders.Recent Pat Nanotechnol. 2025;19(1):17-34. doi: 10.2174/1872210517666230718115651. Recent Pat Nanotechnol. 2025. PMID: 37464820 Review.
-
Synthetic cells in biomedical applications.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2022 Mar;14(2):e1761. doi: 10.1002/wnan.1761. Epub 2021 Nov 1. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2022. PMID: 34725945 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kerr S, Brosnan MJ, McIntyre M, Reid JL, Dominiczak AF, Hamilton CA. Superoxide anion production is increased in a model of genetic hypertension: role of the endothelium. Hypertension. 1999;33(6):1353–1358. - PubMed
-
- Miller FJ, Jr., Gutterman DD, Rios CD, Heistad DD, Davidson BL. Superoxide production in vascular smooth muscle contributes to oxidative stress and impaired relaxation in atherosclerosis. Circ Res. 1998;82(12):1298–1305. - PubMed
-
- Mugge A, Brandes RP, Boger RH, Dwenger A, Bode-Boger S, Kienke S, Frolich JC, Lichtlen PR. Vascular release of superoxide radicals is enhanced in hypercholesterolemic rabbits. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1994;24(6):994–998. - PubMed
-
- Forman LJ, Liu P, Nagele RG, Yin K, Wong PY. Augmentation of nitric oxide, superoxide, and peroxynitrite production during cerebral ischemia and reperfusion in the rat. Neurochem Res. 1998;23(2):141–148. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
