Immunodeficiency scoring index to predict poor outcomes in hematopoietic cell transplant recipients with RSV infections
- PMID: 24700783
- PMCID: PMC4046424
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2013-12-541359
Immunodeficiency scoring index to predict poor outcomes in hematopoietic cell transplant recipients with RSV infections
Abstract
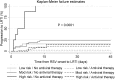
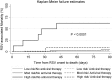
We developed an immunodeficiency scoring index for respiratory syncytial virus (ISI-RSV) infection, based on a cohort of 237 allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplant (allo-HCT) recipients, that can predict the risk of progression to lower respiratory tract infection (LRTI) and RSV-associated mortality. A weighted index was calculated using adjusted hazard ratios for immunodeficiency markers. Based on the ISI-RSV (range, 0-12), patients were stratified into low (0-2), moderate (3-6), and high (7-12) risk groups. A significant trend of increasing incidence of LRTI and RSV-associated mortality was observed as the risk increased from low to moderate to high (P < .001). Patients in the high-risk group had the greatest benefit of ribavirin-based therapy at the upper respiratory tract infection stage and the highest risk for progression to LRTI and death when antiviral therapy was not given (6.5 [95% confidence interval (CI), 1.8-23.6] and 8.1 [95% CI, 1.1-57.6], respectively). The ISI-RSV is designed to stratify allo-HCT recipients with RSV infection into groups according to their risk for progression to LRTI and RSV-associated mortality. Identification of high-risk groups using this index would distinguish patients who would benefit the most from antiviral therapy, mainly with aerosolized ribavirin. The ISI-RSV should be validated in a multi-institutional study.
© 2014 by The American Society of Hematology.
Figures

References
-
- Shah JN, Chemaly RF. Management of RSV infections in adult recipients of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood. 2011;117(10):2755–2763. - PubMed
-
- Martino R, Porras RP, Rabella N, et al. Prospective study of the incidence, clinical features, and outcome of symptomatic upper and lower respiratory tract infections by respiratory viruses in adult recipients of hematopoietic stem cell transplants for hematologic malignancies. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2005;11(10):781–796. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chemaly RF, Ghosh S, Bodey GP, et al. Respiratory viral infections in adults with hematologic malignancies and human stem cell transplantation recipients: a retrospective study at a major cancer center. Medicine (Baltimore) 2006;85(5):278–287. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

