A protein kinase A-independent pathway controlling aquaporin 2 trafficking as a possible cause for the syndrome of inappropriate antidiuresis associated with polycystic kidney disease 1 haploinsufficiency
- PMID: 24700872
- PMCID: PMC4178447
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2013111234
A protein kinase A-independent pathway controlling aquaporin 2 trafficking as a possible cause for the syndrome of inappropriate antidiuresis associated with polycystic kidney disease 1 haploinsufficiency
Abstract
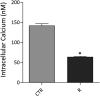
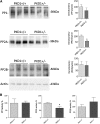
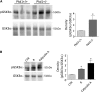
Renal water reabsorption is controlled by arginine vasopressin (AVP), which binds to V2 receptors, resulting in protein kinase A (PKA) activation, phosphorylation of aquaporin 2 (AQP2) at serine 256, and translocation of AQP2 to the plasma membrane. However, AVP also causes dephosphorylation of AQP2 at S261. Recent studies showed that cyclin-dependent kinases (cdks) can phosphorylate AQP2 peptides at S261 in vitro. We investigated the possible role of cdks in the phosphorylation of AQP2 and identified a new PKA-independent pathway regulating AQP2 trafficking. In ex vivo kidney slices and MDCK-AQP2 cells, R-roscovitine, a specific inhibitor of cdks, increased pS256 levels and decreased pS261 levels. The changes in AQP2 phosphorylation status were paralleled by increases in cell surface expression of AQP2 and osmotic water permeability in the absence of forskolin stimulation. R-Roscovitine did not alter cAMP-dependent PKA activity but specifically reduced protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) expression and activity in MDCK cells. Notably, we found reduced PP2A expression and activity and reduced pS261 levels in Pkd1(+/-) mice displaying a syndrome of inappropriate antidiuresis with high levels of pS256, despite unchanged AVP and cAMP. Similar to previous findings in Pkd1(+/-) mice, R-roscovitine treatment caused a significant decrease in intracellular calcium in MDCK cells. Our data indicate that reduced activity of PP2A, secondary to reduced intracellular Ca(2+) levels, promotes AQP2 trafficking independent of the AVP-PKA axis. This pathway may be relevant for explaining pathologic states characterized by inappropriate AVP secretion and positive water balance.
Copyright © 2014 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures





Similar articles
-
PKD1 haploinsufficiency causes a syndrome of inappropriate antidiuresis in mice.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007 Jun;18(6):1740-53. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2006010052. Epub 2007 May 2. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007. PMID: 17475819
-
Psychotropic drugs upregulate aquaporin-2 via vasopressin-2 receptor/cAMP/protein kinase A signaling in inner medullary collecting duct cells.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2021 May 1;320(5):F963-F971. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00576.2020. Epub 2021 Apr 12. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33843270
-
Inhibition of non-receptor tyrosine kinase Src induces phosphoserine 256-independent aquaporin-2 membrane accumulation.J Physiol. 2019 Mar;597(6):1627-1642. doi: 10.1113/JP277024. Epub 2018 Dec 21. J Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30488437 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of aquaporin-2 trafficking.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2009;(190):133-57. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-79885-9_6. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19096775 Review.
-
Activation of AQP2 water channels by protein kinase A: therapeutic strategies for congenital nephrogenic diabetes insipidus.Clin Exp Nephrol. 2021 Oct;25(10):1051-1056. doi: 10.1007/s10157-021-02108-6. Epub 2021 Jul 5. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2021. PMID: 34224008 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of protein phosphatase 2A in kidney disease (Review).Exp Ther Med. 2021 Nov;22(5):1236. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.10671. Epub 2021 Aug 31. Exp Ther Med. 2021. PMID: 34539832 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Collecting duct water permeability inhibition by EGF is associated with decreased cAMP, PKA activity, and AQP2 phosphorylation at Ser269.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2024 Mar 1;326(3):F545-F559. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00197.2023. Epub 2024 Jan 11. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38205543 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms regulating aquaporin-2 in kidney collecting duct.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2016 Dec 1;311(6):F1318-F1328. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00485.2016. Epub 2016 Oct 19. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27760771 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Olive Leaf Extract (OLE) impaired vasopressin-induced aquaporin-2 trafficking through the activation of the calcium-sensing receptor.Sci Rep. 2021 Feb 25;11(1):4537. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-83850-5. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33633156 Free PMC article.
-
EGF Receptor Inhibition by Erlotinib Increases Aquaporin 2-Mediated Renal Water Reabsorption.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016 Oct;27(10):3105-3116. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2015080903. Epub 2016 Mar 9. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 27694161 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Valenti G, Procino G, Tamma G, Carmosino M, Svelto M: Minireview: Aquaporin 2 trafficking. Endocrinology 146: 5063–5070, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Fenton RA, Pedersen CN, Moeller HB: New insights into regulated aquaporin-2 function. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 22: 551–558, 2013 - PubMed
-
- Ahrabi AK, Terryn S, Valenti G, Caron N, Serradeil-Le Gal C, Raufaste D, Nielsen S, Horie S, Verbavatz JM, Devuyst O: PKD1 haploinsufficiency causes a syndrome of inappropriate antidiuresis in mice. J Am Soc Nephrol 18: 1740–1753, 2007 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

