Mutations in SLC34A3/NPT2c are associated with kidney stones and nephrocalcinosis
- PMID: 24700880
- PMCID: PMC4178443
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2013101085
Mutations in SLC34A3/NPT2c are associated with kidney stones and nephrocalcinosis
Abstract
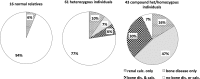
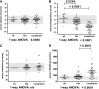
Compound heterozygous and homozygous (comp/hom) mutations in solute carrier family 34, member 3 (SLC34A3), the gene encoding the sodium (Na(+))-dependent phosphate cotransporter 2c (NPT2c), cause hereditary hypophosphatemic rickets with hypercalciuria (HHRH), a disorder characterized by renal phosphate wasting resulting in hypophosphatemia, correspondingly elevated 1,25(OH)2 vitamin D levels, hypercalciuria, and rickets/osteomalacia. Similar, albeit less severe, biochemical changes are observed in heterozygous (het) carriers and indistinguishable from those changes encountered in idiopathic hypercalciuria (IH). Here, we report a review of clinical and laboratory records of 133 individuals from 27 kindreds, including 5 previously unreported HHRH kindreds and two cases with IH, in which known and novel SLC34A3 mutations (c.1357delTTC [p.F453del]; c.G1369A [p.G457S]; c.367delC) were identified. Individuals with mutations affecting both SLC34A3 alleles had a significantly increased risk of kidney stone formation or medullary nephrocalcinosis, namely 46% compared with 6% observed in healthy family members carrying only the wild-type SLC34A3 allele (P=0.005) or 5.64% in the general population (P<0.001). Renal calcifications were also more frequent in het carriers (16%; P=0.003 compared with the general population) and were more likely to occur in comp/hom and het individuals with decreased serum phosphate (odds ratio [OR], 0.75, 95% confidence interval [95% CI], 0.59 to 0.96; P=0.02), decreased tubular reabsorption of phosphate (OR, 0.41; 95% CI, 0.23 to 0.72; P=0.002), and increased serum 1,25(OH)2 vitamin D (OR, 1.22; 95% CI, 1.05 to 1.41; P=0.008). Additional studies are needed to determine whether these biochemical parameters are independent of genotype and can guide therapy to prevent nephrocalcinosis, nephrolithiasis, and potentially, CKD.
Copyright © 2014 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures

References
-
- Bergwitz C, Roslin NM, Tieder M, Loredo-Osti JC, Bastepe M, Abu-Zahra H, Frappier D, Burkett K, Carpenter TO, Anderson D, Garabedian M, Sermet I, Fujiwara TM, Morgan K, Tenenhouse HS, Jüppner H: SLC34A3 mutations in patients with hereditary hypophosphatemic rickets with hypercalciuria predict a key role for the sodium-phosphate cotransporter NaPi-IIc in maintaining phosphate homeostasis. Am J Hum Genet 78: 179–192, 2006 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lorenz-Depiereux B, Benet-Pages A, Eckstein G, Tenenbaum-Rakover Y, Wagenstaller J, Tiosano D, Gershoni-Baruch R, Albers N, Lichtner P, Schnabel D, Hochberg Z, Strom TM: Hereditary hypophosphatemic rickets with hypercalciuria is caused by mutations in the sodium-phosphate cotransporter gene SLC34A3. Am J Hum Genet 78: 193–201, 2006 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ichikawa S, Sorenson AH, Imel EA, Friedman NE, Gertner JM, Econs MJ: Intronic deletions in the SLC34A3 gene cause hereditary hypophosphatemic rickets with hypercalciuria. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 91: 4022–4027, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Tieder M, Modai D, Samuel R, Arie R, Halabe A, Bab I, Gabizon D, Liberman UA: Hereditary hypophosphatemic rickets with hypercalciuria. N Engl J Med 312: 611–617, 1985 - PubMed
-
- Tieder M, Modai D, Shaked U, Samuel R, Arie R, Halabe A, Maor J, Weissgarten J, Averbukh Z, Cohen N, Edelstein S, Liberman UA: “Idiopathic” hypercalciuria and hereditary hypophosphatemic rickets. Two phenotypical expressions of a common genetic defect. N Engl J Med 316: 125–129, 1987 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

