Dexmedetomidine versus midazolam for conscious sedation in endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography: An open-label randomised controlled trial
- PMID: 24700894
- PMCID: PMC3968645
- DOI: 10.4103/0019-5049.126782
Dexmedetomidine versus midazolam for conscious sedation in endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography: An open-label randomised controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Traditionally, midazolam has been used for providing conscious sedation in endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP). Recently, dexmedetomidine has been tried, but very little evidence exists to support its use.
Objective: The primary objective was to compare haemodynamic, respiratory and recovery profile of both drugs. Secondary objective was to compare the degree of comfort experienced by patients and the usefulness of the drug to endoscopist.
Study design: Open-label Randomised Controlled Trial.
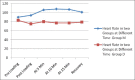
Methods: Subjects between 18 and 60 years of age with American Society of Anaesthesiologist Grade I-II requiring ERCP were enrolled in two groups (30 each). Both groups received fentanyl 1 μg/kg IV at the beginning of ERCP. Group M received IV midazolam (0.04 mg/kg) and additional 0.5 mg doses until Ramsay Sedation Scale (RSS) score reached 3-4. Group D received dexmedetomidine at loading dose of 1 μg/kg over 10 min followed by 0.5 μg/kg/h infusion until RSS reached 3-4. The vital parameters (heart rate (HR), blood pressure (BP), respiration rate, SpO2), time to achieve RSS 3-4 and facial pain score (FPS) were compared during and after the procedure. In the recovery room, time to reach modified Aldrete score (MAS) 9-10 and patient and surgeon's satisfaction scores was also recorded and compared. Any complication during or after the procedure were also noted.
Results: In Group D, patients had lower HR and FPS at 5, 10 and 15 min following the initiation of sedation (P<0.05). There was no statistically significant difference in BP and respiratory rate. The procedure elicited a gag response in 29 (97%) and 7 (23%) subjects in Group M and Group D respectively (P<0.05). MAS of 9-10 at 5 min during recovery was achieved in 27 (90%) subjects in Group D in contrast to 5 (17%) in Group M (P<0.05). Dexmedetomidine showed higher patient and surgeon satisfaction scores (P<0.05).
Conclusion: Dexmedetomidine can be a superior alternative to midazolam for conscious sedation in ERCP.
Keywords: Conscious sedation; dexmedetomidine; endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography; midazolam.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Chen WX, Lin HJ, Zhang WF, Gu Q, Zhong XQ, Yu CH, et al. Sedation and safety of propofol for therapeutic endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2005;4:437–40. - PubMed
-
- American Society of Anesthesiologists. Continuum of Depth of Sedation: Definition of General Anesthesia and Levels of Sedation/Analgesia. 2004. [Last accessed on 2011 Nov 12]. Available from: http://www.asahq.org/publications and services/standards/20.pdf .
-
- Froehlich F, Schwizer W, Thorens J, Köhler M, Gonvers JJ, Fried M. Conscious sedation for gastroscopy: Patient tolerance and cardiorespiratory parameters. Gastroenterology. 1995;108:697–704. - PubMed
-
- Zakko SF, Seifert HA, Gross JB. A comparison of midazolam and diazepam for conscious sedation during colonoscopy in a prospective double-blind study. Gastrointest Endosc. 1999;49:684–9. - PubMed
-
- Muller S, Borowics SM, Fortis EA, Stefani LC, Soares G, Maguilnik I, et al. Clinical efficacy of dexmedetomidine alone is less than propofol for conscious sedation during ERCP. Gastrointest Endosc. 2008;67:651–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous