A comparative study between intrathecal clonidine and neostigmine with intrathecal bupivacaine for lower abdominal surgeries
- PMID: 24700898
- PMCID: PMC3968650
- DOI: 10.4103/0019-5049.126794
A comparative study between intrathecal clonidine and neostigmine with intrathecal bupivacaine for lower abdominal surgeries
Abstract
Background and aims: Spinal anaesthesia requires a small volume of drug to produce profound reproducible sensory analgesia and motor blockade, but has limited duration of action. A properly chosen adjuvant to local anaesthetic agent produces the best way to achieve a better quality regional block. Hence, a study was conducted to compare the effect of intrathecal clonidine 75 μg or neostigmine 50 μg added to intrathecal hyperbaric bupivacaine, with regards to sensory characteristics, motor characteristics, haemodynamic stability and side effects.
Methods: This was a prospective randomized experimental study in 50 patients posted for lower abdominal surgery belonging to ASA I and II status and aged between18 and 60 years. One group received intrathecal clonidine 75 μg and 2.5 ml (12.5 mg) of intrathecal 0.5% hyperbaric bupivacaine (group BC) and second group received neostigmine 50 μg with 2.5 ml (12.5mg) of intrathecal 0.5% hyperbaric bupivacaine (group BN) and they were compared with regards to sensory characteristics, motor characteristics, haemodynamic stability and side effects.
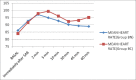
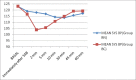
Results: Addition of 50 μg neostigmine significantly enhanced the onset of sensory block (BN - 90 ± 15 secs, BC-160 ± 20 secs, P value as <0.05) and motor block (BN-110 ± 15 secs, BC-210 ± 20 secs, P value as <0.05) compared to clonidine. Haemodynamics were well maintained in the neostigmine group. Group BC had prolonged analgesia (362 ± 36 mins) compared to BN group (300 ± 25 mins)(P < 0.05) with no serious adverse effects noted perioperatively in either groups.
Conclusion: Intrathecal clonidine with hyperbaric bupivacaine produces prolonged postoperative analgesia and intrathecal neostigmine with bupivacaine produces a good sensory and motor for the surgical procedure.
Keywords: Analgesia; bromage scale; clonidine; hyperbaric; lower abdominal surgery; neostigmine.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Eisenach JC, De Kock M, Klimscha W. Alpha (2)-adrenergic agonists for regional anesthesia: A clinical review of Clonidine. Anesthesiology. 1996;85:655–74. - PubMed
-
- Strebel S, Gurzeler JA, Schneider MC, Aeschbach A, Kindler CH. Small- dose Intrathecal Clonidine and Isobaric Bupivacaine for Orthopaedic surgery: A dose response study. Anesth Analg. 2004;99:1231–8. - PubMed
-
- Bouaziz H, Tong C, Eisenach JC. Post operative analgesia from intrathecal Neostigmine in sheep. Anesth Analg. 1995;80:1140–4. - PubMed
-
- Bromage PR. Philadelphia: WB Saunders; 1978. Epidural analgesia; p. 144.
-
- Siddall PJ, Molloy AR, Walker S, Mather LE, Rutkowski SB, Cousins MJ. The efficacy of Intrathecal Morphine and Clonidine in the treatment of pain after spinal cord injury. Anesth Analg. 2000;91:1493–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources