Video traffic characteristics of modern encoding standards: H.264/AVC with SVC and MVC extensions and H.265/HEVC
- PMID: 24701145
- PMCID: PMC3951063
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/189481
Video traffic characteristics of modern encoding standards: H.264/AVC with SVC and MVC extensions and H.265/HEVC
Abstract
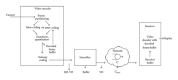
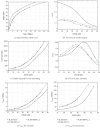
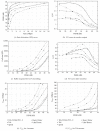
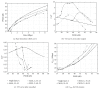
Video encoding for multimedia services over communication networks has significantly advanced in recent years with the development of the highly efficient and flexible H.264/AVC video coding standard and its SVC extension. The emerging H.265/HEVC video coding standard as well as 3D video coding further advance video coding for multimedia communications. This paper first gives an overview of these new video coding standards and then examines their implications for multimedia communications by studying the traffic characteristics of long videos encoded with the new coding standards. We review video coding advances from MPEG-2 and MPEG-4 Part 2 to H.264/AVC and its SVC and MVC extensions as well as H.265/HEVC. For single-layer (nonscalable) video, we compare H.265/HEVC and H.264/AVC in terms of video traffic and statistical multiplexing characteristics. Our study is the first to examine the H.265/HEVC traffic variability for long videos. We also illustrate the video traffic characteristics and statistical multiplexing of scalable video encoded with the SVC extension of H.264/AVC as well as 3D video encoded with the MVC extension of H.264/AVC.
Figures

Similar articles
-
High efficiency video coding for ultrasound video communication in m-health systems.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2012;2012:2170-3. doi: 10.1109/EMBC.2012.6346391. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2012. PMID: 23366352
-
Improved lossless intra coding for H.264/MPEG-4 AVC.IEEE Trans Image Process. 2006 Sep;15(9):2610-5. doi: 10.1109/tip.2006.877396. IEEE Trans Image Process. 2006. PMID: 16948306
-
An effective ultrasound video communication system using despeckle filtering and HEVC.IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2015 Mar;19(2):668-76. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2014.2329572. Epub 2014 Jun 6. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2015. PMID: 24951708
-
Streaming video transforms the media industry.IEEE Comput Graph Appl. 2004 Jul-Aug;24(4):6-12. doi: 10.1109/mcg.2004.17. IEEE Comput Graph Appl. 2004. PMID: 15628079 Review. No abstract available.
-
Machine Learning for Multimedia Communications.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Jan 21;22(3):819. doi: 10.3390/s22030819. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35161566 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Real-Time Compression for Tactile Internet Data Streams.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Mar 9;21(5):1924. doi: 10.3390/s21051924. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33803484 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Tensor Ring Sparsity Measurement for Image Completion.Entropy (Basel). 2024 Jan 24;26(2):105. doi: 10.3390/e26020105. Entropy (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38392360 Free PMC article.
-
A Secure Video Steganography Based on the Intra-Prediction Mode (IPM) for H264.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Sep 14;20(18):5242. doi: 10.3390/s20185242. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32937998 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of blocking rate and bandwidth usage of mobile IPTV services in wireless cellular networks.ScientificWorldJournal. 2014;2014:215710. doi: 10.1155/2014/215710. Epub 2014 Oct 14. ScientificWorldJournal. 2014. PMID: 25379521 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cisco I. Cisco Visual Networking Index: Forecast and Methodology, 2011–2016. 2012.
-
- Wiegand T, Sullivan GJ, Bjøntegaard G, Luthra A. Overview of the H.264/AVC video coding standard. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology. 2003;13(7):560–576.
-
- Ohm JR, Sullivan GJ. High efficiency video coding: the next frontier in video compression [standards in a nutshell] IEEE Signal Processing Magazine. 2013;30(1):152–158.
-
- Henot JP, Ropert M, Le Tanou J, Kypreos J, Guionnet T. High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC): replacing or complementing existing compression standards?. Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Broadband Multimedia Systems and Broadcasting (BMSB '13); 2013; pp. 1–6.
-
- Sullivan G, Ohm JR, Han WJ, Wiegand T. Overview of the High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC) standard. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems For Video Technology. 2012;22(12):1649–1668.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

