The diamagnetic susceptibility of the tubulin dimer
- PMID: 24701206
- PMCID: PMC3948583
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/985082
The diamagnetic susceptibility of the tubulin dimer
Abstract
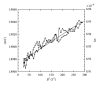
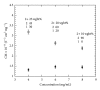
An approximate value of the diamagnetic anisotropy of the tubulin dimer, Δχ dimer, has been determined assuming axial symmetry and that only the α -helices and β -sheets contribute to the anisotropy. Two approaches have been utilized: (a) using the value for the Δχ α for an α -helical peptide bond given by Pauling (1979) and (b) using the previously determined anisotropy of fibrinogen as a calibration standard. The Δχ dimer ≈ 4 × 10(-27) JT(-2) obtained from these measurements are similar to within 20%. Although Cotton-Mouton measurements alone cannot be used to estimate Δχ directly, the value we measured, CMdimer = (1.41 ± 0.03) × 10(-8) T(-2)cm(2)mg(-1), is consistent with the above estimate for Δχ dimer. The method utilized for the determination of the tubulin dimer diamagnetic susceptibility is applicable to other proteins and macromolecular assemblies as well.
Figures
References
-
- Vassilev PM, Dronzine RT, Vassileva MP, Georgiev GA. Parallel arrays of microtubules formed in electric and magnetic fields. Bioscience Reports. 1982;2(12):1025–1029. - PubMed
-
- Torbet J. Using magnetic orientation to study structure and assembly. Trends in Biochemical Sciences C. 1987;12:327–330.
-
- Maret G, Dransfeld K. Strong and Ultrastrong Magnetic Fields and their Applications. Springer; 1985.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

