The complementary and alternative medicine for endometriosis: a review of utilization and mechanism
- PMID: 24701237
- PMCID: PMC3950373
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/146383
The complementary and alternative medicine for endometriosis: a review of utilization and mechanism
Abstract
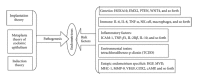
Endometriosis (EM) is one of the common gynecological conditions causing menstrual and pelvic pain and affects 10%-15% of women of reproductive age. In recent years, the complementary and alternative medical (CAM) treatment for EM has become popular due to the few adverse reactions reported. The CAM therapy for EM includes several different treatments such as herbs (herbal prescription, extract, and patent), acupuncture, microwave physiotherapy, and Chinese herb medicine enema (CHM enema). These CAM therapies are effective at relieving dysmenorrhoea, shrinking adnexal masses, and promoting pregnancy, with less unpleasant side effects when compared to hormonal and surgical treatments. In this review, we focus on the status quo of CAM on EM and try to identify therapeutic efficacy and mechanisms based on some clinical and experimental studies. We hope to provide some instructive suggestions for clinical treatment and experimental research in the future.
Figures
References
-
- Giudice LC, Kao LC. Endometriosis. The Lancet. 2004;364(9447):1789–1799. - PubMed
-
- Batt RE. A History of Endometriosis. London, UK: Springer; 2011.
-
- Sinaii N, Cleary SD, Ballweg ML, Nieman LK, Stratton P. High rates of autoimmune and endocrine disorders, fibromyalgia, chronic fatigue syndrome and atopic diseases among women with endometriosis: a survey analysis. Human Reproduction. 2002;17(10):2715–2724. - PubMed
-
- Wellbery C. Diagnosis and treatment of endometriosis. American Family Physician. 1999;60(6):1753–1762. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical