Seoritae extract reduces prostate weight and suppresses prostate cell proliferation in a rat model of benign prostate hyperplasia
- PMID: 24701239
- PMCID: PMC3950473
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/475876
Seoritae extract reduces prostate weight and suppresses prostate cell proliferation in a rat model of benign prostate hyperplasia
Abstract
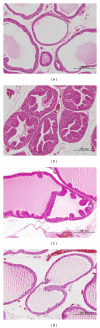
Seoritae is a type of black soybean that is known to have health-promoting effects due to its high isoflavone and anthocyanin contents. We evaluated whether Seoritae extract (SE) had beneficial effects on the reduction of prostate weight in a rat model of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). BPH was induced by intramuscular injections of testosterone enanthate once a week for 5 weeks in Sprague-Dawley rats, and rats were treated with or without daily oral doses of SE during BPH induction. After 5 weeks, the oxidative stress (superoxide dismutase and 8-hydroxy-2-deoxyguanosine), apoptosis (caspase-3), and activity of 5-alpha reductase were evaluated in the serum and prostate. The SE treatment group showed a significant decrease in prostate weight, oxidative stress, apoptosis, and 5-alpha reductase activity compared to the nontreated BPH group. These results show that SE is effective in decreasing the weight and proliferation of the prostate, and suggest that SE may be an effective treatment for BPH.
Figures

References
-
- Arias E. United States life tables, 2007. National Vital Statistics Reports. 2011;59(9):1–60. - PubMed
-
- Carson C, III, Rittmaster R. The role of dihydrotestosterone in benign prostatic hyperplasia. Urology. 2003;61(4):2–7. - PubMed
-
- Aryal M, Pandeya A, Gautam N, et al. Oxidative stress in benign prostate hyperplasia. Nepal Medical College Journal. 2007;9(4):222–224. - PubMed
-
- Aydin A, Arsova-Sarafinovska Z, Sayal A, et al. Oxidative stress and antioxidant status in non-metastatic prostate cancer and benign prostatic hyperplasia. Clinical Biochemistry. 2006;39(2):176–179. - PubMed
-
- Jang H, Ha U-S, Kim S-J, et al. Anthocyanin extracted from black soybean reduces prostate weight and promotes apoptosis in the prostatic hyperplasia-induced rat model. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 2010;58(24):12686–12691. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

