Prognostic categorization of intensive care septic patients
- PMID: 24701404
- PMCID: PMC3953866
- DOI: 10.5492/wjccm.v1.i3.67
Prognostic categorization of intensive care septic patients
Abstract
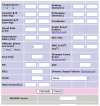
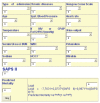
Sepsis is one of the leading worldwide causes of morbidity and mortality in critically-ill patients. Prediction of outcome in patients with sepsis requires repeated clinical interpretation of the patients' conditions, clinical assessment of tissue hypoxia and the use of severity scoring systems, because the prognostic categorization accuracy of severity scoring indices alone, is relatively poor. Generally, such categorization depends on the severity of the septic state, ranging from systemic inflammatory response to septic shock. Now, there is no gold standard for the clinical assessment of tissue hypoxia which can be achieved by both global and regional oxygen extractabilities, added to prognostic pro-inflammatory mediators. Because the technology used to identify the genetic make-up of the human being is rapidly advancing, the structure of 30 000 genes which make-up the human DNA bank is now known. This would allow easy prognostic categorization of critically-ill patients including those suffering from sepsis. The present review spots lights on the main severity scoring systems used for outcome prediction in septic patients. For morbidity prediction, it discusses the Multiple Organ Dysfunction score, the sequential organ failure assessment score, and the logistic organ dysfunction score. For mortality/survival prediction, it discusses the Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation scores, the Therapeutic Intervention Scoring System, the Simplified acute physiology score and the Mortality Probability Models. An ideal severity scoring system for prognostic categorization of patients with systemic sepsis is far from being reached. Scoring systems should be used with repeated clinical interpretation of the patients' conditions, and the assessment of tissue hypoxia in order to attain satisfactory discriminative performance and calibration power.
Keywords: Genome; Prognostic markers; Sepsis; Severity scoring systems; Systemic inflammatory Response syndrome.
Figures



References
-
- Bone RC, Balk RA, Cerra FB, Dellinger RP, Fein AM, Knaus WA, Schein RM, Sibbald WJ. Definitions for sepsis and organ failure and guidelines for the use of innovative therapies in sepsis. The ACCP/SCCM Consensus Conference Committee. American College of Chest Physicians/Society of Critical Care Medicine. Chest. 1992;101:1644–1655. - PubMed
-
- Rangel-Frausto MS, Pittet D, Costigan M, Hwang T, Davis CS, Wenzel RP. The natural history of the systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS). A prospective study. JAMA. 1995;273:117–123. - PubMed
-
- Le Gall JR, Lemeshow S, Leleu G, Klar J, Huillard J, Rué M, Teres D, Artigas A. Customized probability models for early severe sepsis in adult intensive care patients. Intensive Care Unit Scoring Group. JAMA. 1995;273:644–650. - PubMed
-
- Marshall JC, Cook DJ, Christou NV, Bernard GR, Sprung CL, Sibbald WJ. Multiple organ dysfunction score: a reliable descriptor of a complex clinical outcome. Crit Care Med. 1995;23:1638–1652. - PubMed
-
- Webster NR. Activated protein C in sepsis. AJAIC. 2001;4(Suppl 1):41–42.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

