Small dense low-density lipoprotein as a potential risk factor of nephropathy in type 2 diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 24701437
- PMCID: PMC3968741
- DOI: 10.4103/2230-8210.126585
Small dense low-density lipoprotein as a potential risk factor of nephropathy in type 2 diabetes mellitus
Abstract
Background: The risk for diabetic nephropathy in type 2 diabetes is about 30-40%, and it is considered the leading cause of end-stage renal disease. Small dense low-density lipoprotein (sdLDL) particles are believed to be atherogenic, and its predominance has been accepted as an emerging cardiovascular risk factor. This study aimed to assess small dense LDL as a potential risk factor and a possible predictor for diabetic nephropathy in type 2 diabetic patients.
Patients and methods: According to microalbuminuria test, 40 diabetic patients were categorized into two groups: Diabetic patients without nephropathy (microalbuminuria negative group) and diabetic patients with nephropathy (microalbuminuria positive group), each group consists of 20 patients and all were non-obese and normotensive. The patients were re-classified into three sub-groups depending on the glomerular filtration rate (GFR).
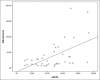
Results: The mean of small dense LDL level in the microalbuminuria positive group was higher than that in the microalbuminuria negative group, but without statistical significance. It was significantly higher in patients with either mild or moderate decrease in estimated GFR than in patients with normal estimated GFR. There was statistically significant correlation between small dense LDL and albuminuria and significant inverse correlation between small dense LDL and estimated GFR in all patients in the study. Based on microalbuminuria, the sensitivity and specificity of small dense LDL in the diagnosis of diabetic nephropathy was 40% and 80%, respectively, with cutoff values of small dense LDL >55.14 mg/dl. On the other hand, based on GFR, the sensitivity and specificity were 88.24% and 73.91% respectively, with cutoff values of small dense LDL >41.89 mg/dl.
Conclusion: Small dense LDL is correlated with the incidence and severity of diabetic nephropathy in type 2 diabetic patients. It should be considered as a potential risk factor and as a diagnostic biomarker to be used in conjunction with other biochemical markers for early diagnosis, assessment, and follow-up of diabetic nephropathy.
Keywords: Albuminuria; diabetes mellitus; diabetic nephropathy; small dense LDL.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- King H, Aubert RE, Herman WH. Global Burden of Diabetes, 1995-2025: Prevalence, numerical estimates, and projections. Diabetes Care. 1998;21:1414–31. - PubMed
-
- Zoungas S, de Galan BE, Ninomiya T, Grobbee D, Hamet P, Heller, et al. Combined effects of routine blood pressure lowering and intensive glucose control on macrovascular and microvascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes: New results from the ADVANCE trial group. Diabetes Care. 2009;32:2068–74. - PMC - PubMed
-
- LeRoith D, Fonseca V, Vinik A. Metabolic memory in diabetes-focus on insulin. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2005;21:85–90. - PubMed
-
- Anselmino m, Sillano D. The impact of pre-diabetes and diabetes on cardiovascular outcomes. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2012;10(6):680–3. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources