Proton pump inhibition increases rapid eye movement sleep in the rat
- PMID: 24701564
- PMCID: PMC3950396
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/162314
Proton pump inhibition increases rapid eye movement sleep in the rat
Abstract
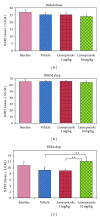
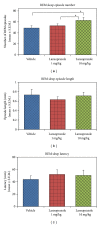
Increased bodily CO2 concentration alters cellular pH as well as sleep. The proton pump, which plays an important role in the homeostatic regulation of cellular pH, therefore, may modulate sleep. We investigated the effects of the proton pump inhibitor "lansoprazole" on sleep-wakefulness. Male Wistar rats were surgically prepared for chronic polysomnographic recordings. Two different doses of lansoprazole (low: 1 mg/kg; high: 10 mg/kg) were injected intraperitoneally in the same animal (n = 7) and sleep-wakefulness was recorded for 6 hrs. The changes in sleep-wakefulness were compared statistically. Percent REM sleep amount in the vehicle and lansoprazole low dose groups was 9.26 ± 1.03 and 9.09 ± 0.54, respectively, which increased significantly in the lansoprazole high dose group by 31.75% (from vehicle) and 34.21% (from low dose). Also, REM sleep episode numbers significantly increased in lansoprazole high dose group. Further, the sodium-hydrogen exchanger blocker "amiloride" (10 mg/kg; i.p.) (n = 5) did not alter sleep-wake architecture. Our results suggest that the proton pump plays an important role in REM sleep modulation and supports our view that REM sleep might act as a sentinel to help maintain normal CO2 level for unperturbed sleep.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Locus Coeruleus Acid-Sensing Ion Channels Modulate Sleep-Wakefulness and State Transition from NREM to REM Sleep in the Rat.Neurosci Bull. 2021 May;37(5):684-700. doi: 10.1007/s12264-020-00625-0. Epub 2021 Feb 27. Neurosci Bull. 2021. PMID: 33638800 Free PMC article.
-
Proton Pump Inhibitor "Lansoprazole" Inhibits Locus Coeruleus's Neuronal Activity and Increases Rapid Eye Movement Sleep.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2021 Nov 17;12(22):4265-4274. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.1c00185. Epub 2021 Nov 3. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34730349
-
The Kir channel in the nucleus tractus solitarius integrates the chemosensory system with REM sleep executive machinery for homeostatic balance.Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 17;14(1):21651. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-71818-0. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39289431 Free PMC article.
-
[Selective stimulations and lesions of the rat brain nuclei as the models for research of the human sleep pathology mechanisms].Glas Srp Akad Nauka Med. 2011;(51):85-97. Glas Srp Akad Nauka Med. 2011. PMID: 22165729 Review. Serbian.
-
Neural Circuitry of Wakefulness and Sleep.Neuron. 2017 Feb 22;93(4):747-765. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2017.01.014. Neuron. 2017. PMID: 28231463 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Locus Coeruleus Acid-Sensing Ion Channels Modulate Sleep-Wakefulness and State Transition from NREM to REM Sleep in the Rat.Neurosci Bull. 2021 May;37(5):684-700. doi: 10.1007/s12264-020-00625-0. Epub 2021 Feb 27. Neurosci Bull. 2021. PMID: 33638800 Free PMC article.
-
Proton pump inhibitors associated with rapid eye movement sleep behaviour disorder.BMJ Case Rep. 2021 Dec 31;14(12):e246469. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2021-246469. BMJ Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 34972777 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Breton S, Brown D. New insights into the regulation of V-ATPase-dependent proton secretion. American Journal of Physiology. 2007;292(1):F1–F10. - PubMed
-
- Melville C, Shah A, Matthew D, Milla P. Electrolyte disturbance with omeprazole therapy. European Journal of Pediatrics. 1994;153(1):49–51. - PubMed
-
- Gluck SL, Underhill DM, Iyori M, Holliday LS, Kostrominova TY, Lee BS. Physiology and biochemistry of the kidney vacuolar H+-ATPase. Annual Review of Physiology. 1996;58:427–445. - PubMed
-
- Hashioka S, Klegeris A, McGeer PL. Proton pump inhibitors exert anti-inflammatory effects and decrease human microglial and monocytic THP-1 cell neurotoxicity. Experimental Neurology. 2009;217(1):177–183. - PubMed
-
- Insogna KL. The effect of proton pump-inhibiting drugs on mineral metabolism. The American Journal of Gastroenterology. 2009;104(supplement 2):S2–S4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

