Oxytocin receptor gene polymorphism (rs53576) moderates the intergenerational transmission of depression
- PMID: 24703166
- PMCID: PMC3979470
- DOI: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2014.01.012
Oxytocin receptor gene polymorphism (rs53576) moderates the intergenerational transmission of depression
Abstract
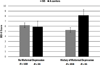
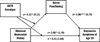
Maternal depression serves as a potent source of stress among offspring, greatly enhancing the risk of numerous adverse outcomes including youth depression. Several factors moderate the transmission of depression from mothers to offspring. However, the role of genetic characteristics in this process merits further exploration. Consistent with an interpersonal perspective on depression, the present study focused on a genetic polymorphism that has been shown to be relevant to social functioning, the rs53576 polymorphism of the oxytocin receptor gene (OXTR). In a community sample of 441 youth, OXTR genotype moderated the association between maternal depression in early childhood and youth depressive symptoms in adolescence, such that youth possessing at least one A allele of OXTR who also had a history of maternal depression exhibited the highest levels of depressive symptoms at age 15. In order to explore possible interpersonal mediators of this effect, conditional process analyses examined the role of youth social functioning in adolescence. Results suggest that OXTR genotype may partially account for the transmission of maternal depression to youth and support the role of dysfunctional social processes as a mechanism through which OXTR influences the development of depressive symptoms.
Keywords: Adolescents; Intergenerational transmission of depression; Maternal depression; OXTR; Oxytocin receptor gene; Social functioning.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest
All authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bakermans-Kranenburg MJ, van IJzendoorn MH. A sociability gene? Meta-analysis of oxytocin receptor genotype effects in humans. Psychiatr. Genet. in press - PubMed
-
- Beardslee WR, Versage EM, Gladstone TRG. Children of affectively ill parents: A review of the past 10 years. J. Am. Acad. Child. Psy. 1998;37(11):1134–1141. - PubMed
-
- Beck AT, Steer RA, Brown GK. Beck Depression Inventory-II Manual. San Antonio, TX: The Psychological Corporation; 1996.
-
- Bedford A, Foulds G. Delusions-Symptoms-States Inventory of Anxiety and Depression. Windsor, UK: National Foundation for Educational Research; 1978.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

