Epidemiology of gout
- PMID: 24703341
- PMCID: PMC4119792
- DOI: 10.1016/j.rdc.2014.01.001
Epidemiology of gout
Abstract
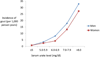
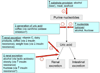
Gout is the most prevalent inflammatory arthritis in men. The findings of several epidemiologic studies from a diverse range of countries suggest that the prevalence of gout has risen over the past few decades. Although incidence data are scarce, data from the United States suggests that the incidence of gout is also rising. Evidence from prospective epidemiologic studies has confirmed dietary factors (animal purines, alcohol, and fructose), obesity, the metabolic syndrome, hypertension, diuretic use, and chronic kidney disease as clinically relevant risk factors for hyperuricemia and gout. Low-fat dairy products, coffee, and vitamin C seem to have a protective effect.
Keywords: Epidemiology; Etiology; Gout; Hyperuricemia; Incidence; Prevalence.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Lawrence RC, Hochberg MC, Kelsey JL, et al. Estimates of the prevalence of selected arthritic and musculoskeletal diseases in the United States. J Rheumatol. 1989;16:427–441. - PubMed
-
- Lawrence RC, Helmick CG, Arnett FC, et al. Estimates of the prevalence of arthritis and selected musculoskeletal disorders in the United States. Arthritis Rheum. 1998;41:778–799. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

