Oligodendrocyte pathophysiology and treatment strategies in cerebral ischemia
- PMID: 24703424
- PMCID: PMC6493108
- DOI: 10.1111/cns.12263
Oligodendrocyte pathophysiology and treatment strategies in cerebral ischemia
Abstract
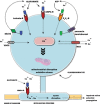
Oligodendrocytes (OLs), the myelin-forming cells of the central nervous system, form a functional unit with axons and play a crucial role in axonal integrity. An episode of hypoxia-ischemia causes rapid and severe damage to these particularly vulnerable cells via multiple pathways such as overactivation of glutamate and ATP receptors, oxidative stress, and disruption of mitochondrial function. The cardinal effect of OL pathology is demyelination and dysmyelination, and this has profound effects on axonal function, transport, structure, metabolism, and survival. The OL is a primary target of ischemia in adult-onset stroke and especially in periventricular leukomalacia and should be considered as a primary therapeutic target in these conditions. More emphasis is needed on therapeutic strategies that target OLs, myelin, and their receptors, as these have the potential to significantly attenuate white matter injury and to establish functional recovery of white matter after stroke. In this review, we will summarize recent progress on the role of OLs in white matter ischemic injury and the current and emerging principles that form the basis for protective strategies against OL death.
Keywords: Excitotoxicity; Hypoxia-ischemia; Oligodendrocyte; Oxidative stress; White matter.
© 2014 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Albert‐Weißenberger C, Sirén AL, Kleinschnitz C. Ischemic stroke and traumatic brain injury: The role of the Kallikrein‐Kinin System. Prog Neurobiol 2013;101–102:65–82. - PubMed
-
- Pantoni L, Garcia JH, Gutierrez JA. Cerebral white matter is highly vulnerable to ischemia. Stroke 1996;27:1641–1647. - PubMed
-
- McTigue DM, Tripathi RB. The life, death, and replacement of oligodendrocytes in the adult CNS. J Neurochem 2008;107:1–19. - PubMed
-
- Merrill JE, Scolding NJ. Mechanisms of damage to myelin and oligodendrocytes and their relevance to disease. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 1999;25:435–458. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

