Intermittent chemotherapy plus either intermittent or continuous cetuximab for first-line treatment of patients with KRAS wild-type advanced colorectal cancer (COIN-B): a randomised phase 2 trial
- PMID: 24703531
- PMCID: PMC4012566
- DOI: 10.1016/S1470-2045(14)70106-8
Intermittent chemotherapy plus either intermittent or continuous cetuximab for first-line treatment of patients with KRAS wild-type advanced colorectal cancer (COIN-B): a randomised phase 2 trial
Abstract
Background: Advanced colorectal cancer is treated with a combination of cytotoxic drugs and targeted treatments. However, how best to minimise the time spent taking cytotoxic drugs and whether molecular selection can refine this further is unknown. The primary aim of this study was to establish how cetuximab might be safely and effectively added to intermittent chemotherapy.
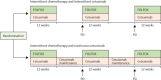
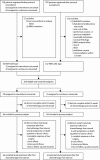
Methods: COIN-B was an open-label, multicentre, randomised, exploratory phase 2 trial done at 30 hospitals in the UK and one in Cyprus. We enrolled patients with advanced colorectal cancer who had received no previous chemotherapy for metastases. Randomisation was done centrally (by telephone) by the Medical Research Council Clinical Trials Unit using minimisation with a random element. Treatment allocation was not masked. Patients were assigned (1:1) to intermittent chemotherapy plus intermittent cetuximab or to intermittent chemotherapy plus continuous cetuximab. Chemotherapy was FOLFOX (folinic acid and oxaliplatin followed by bolus and infused fluorouracil). Patients in both groups received FOLFOX and weekly cetuximab for 12 weeks, then either had a planned interruption (those taking intermittent cetuximab) or planned maintenance by continuing on weekly cetuximab (continuous cetuximab). On RECIST progression, FOLFOX plus cetuximab or FOLFOX was recommenced for 12 weeks followed by further interruption or maintenance cetuximab, respectively. The primary outcome was failure-free survival at 10 months. The primary analysis population consisted of patients who completed 12 weeks of treatment without progression, death, or leaving the trial. We tested BRAF and NRAS status retrospectively. The trial was registered, ISRCTN38375681.
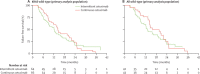
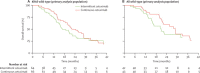
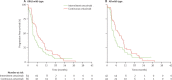
Findings: We registered 401 patients, 226 of whom were enrolled. Results for 169 with KRAS wild-type are reported here, 78 (46%) assigned to intermittent cetuximab and 91 (54%) to continuous cetuximab. 64 patients assigned to intermittent cetuximab and 66 of those assigned to continuous cetuximab were included in the primary analysis. 10-month failure-free survival was 50% (lower bound of 95% CI 39) in the intermittent group versus 52% (lower bound of 95% CI 41) in the continuous group; median failure-free survival was 12.2 months (95% CI 8.8-15.6) and 14.3 months (10.7-20.4), respectively. The most common grade 3-4 adverse events were skin rash (21 [27%] of 77 patients vs 20 [22%] of 92 patients), neutropenia (22 [29%] vs 30 [33%]), diarrhoea (14 [18%] vs 23 [25%]), and lethargy (20 [26%] vs 19 [21%]).
Interpretation: Cetuximab was safely incorporated in two first-line intermittent chemotherapy strategies. Maintenance of biological monotherapy, with less cytotoxic chemotherapy within the first 6 months, in molecularly selected patients is promising and should be validated in phase 3 trials.
Copyright © 2014 Wasan et al. Open Access article distributed under the terms of CC BY. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
Exploring better strategies for EGFR antibodies in colon cancer.Lancet Oncol. 2014 May;15(6):549-50. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(14)70137-8. Epub 2014 Apr 3. Lancet Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24703530 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Addition of cetuximab to oxaliplatin-based first-line combination chemotherapy for treatment of advanced colorectal cancer: results of the randomised phase 3 MRC COIN trial.Lancet. 2011 Jun 18;377(9783):2103-14. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60613-2. Epub 2011 Jun 5. Lancet. 2011. PMID: 21641636 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Cetuximab continuation after first progression in metastatic colorectal cancer (CAPRI-GOIM): a randomized phase II trial of FOLFOX plus cetuximab versus FOLFOX.Ann Oncol. 2016 Jun;27(6):1055-1061. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdw136. Epub 2016 Mar 21. Ann Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27002107 Clinical Trial.
-
Systemic chemotherapy with or without cetuximab in patients with resectable colorectal liver metastasis: the New EPOC randomised controlled trial.Lancet Oncol. 2014 May;15(6):601-11. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(14)70105-6. Epub 2014 Apr 7. Lancet Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24717919 Clinical Trial.
-
Progress in metastatic colorectal cancer: growing role of cetuximab to optimize clinical outcome.Clin Transl Oncol. 2010 Aug;12(8):533-42. doi: 10.1007/s12094-010-0551-3. Clin Transl Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20709651 Review.
-
Anti-EGFR and anti-VEGF agents: important targeted therapies of colorectal liver metastases.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Apr 21;20(15):4263-75. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i15.4263. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 24764664 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A two-stage maintenance trial of cetuximab-based treatment in RAS and BRAF wild-type unresectable metastatic colorectal cancer: a retrospective real-world study.Front Oncol. 2024 Jul 23;14:1425203. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1425203. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39109286 Free PMC article.
-
TRIPLETE: a randomised phase III study of modified FOLFOXIRI plus panitumumab versus mFOLFOX6 plus panitumumab as initial therapy for patients with unresectable RAS and BRAF wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer.ESMO Open. 2018 Jul 9;3(4):e000403. doi: 10.1136/esmoopen-2018-000403. eCollection 2018. ESMO Open. 2018. PMID: 30018814 Free PMC article.
-
A Real-World Retrospective Study to Evaluate the Reliability of Cetuximab plus Capecitabine versus Capecitabine as Maintenance Therapy in Patients with RAS and BRAF Wild-Type Metastatic Colorectal Cancer.Med Princ Pract. 2024;33(1):31-40. doi: 10.1159/000533528. Epub 2023 Sep 19. Med Princ Pract. 2024. PMID: 37725905 Free PMC article.
-
Rechallenge and maintenance therapy using cetuximab and chemotherapy administered to a patient with metastatic colorectal cancer.BMC Cancer. 2017 Feb 14;17(1):132. doi: 10.1186/s12885-017-3133-8. BMC Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28196490 Free PMC article.
-
Final Results of ERBIMOX: A Randomized Phase II Study of Modified FOLFOX7 With or Without Cetuximab as First-Line Treatment for KRAS Wild-type Metastatic Colorectal Cancer.J Gastrointest Cancer. 2025 Jun 27;56(1):141. doi: 10.1007/s12029-025-01260-6. J Gastrointest Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40571867 Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Hecht JR, Mitchell E, Chidiac T. A randomized phase IIIB trial of chemotherapy, bevacizumab, and panitumumab compared with chemotherapy and bevacizumab alone for metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:672–680. - PubMed
-
- Tol J, Koopman M, Cats A. Chemotherapy, bevacizumab, and cetuximab in metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2009;360:563–572. - PubMed
-
- Tveit KM, Guren T, Glimelius B. Phase III trial of cetuximab with continuous or intermittent fluorouracil, leucovorin, and oxaliplatin (Nordic FLOX) versus flox alone in first-line treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer: the NORDIC-VII study. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30:1755–1762. - PubMed
-
- Chibaudel B, Maindrault-Goebel F, Lledo G. Can chemotherapy be discontinued in unresectable metastatic colorectal cancer? The GERCOR OPTIMOX2 study. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:5727–5733. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

