Lysine glutarylation is a protein posttranslational modification regulated by SIRT5
- PMID: 24703693
- PMCID: PMC4108075
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2014.03.014
Lysine glutarylation is a protein posttranslational modification regulated by SIRT5
Abstract
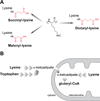
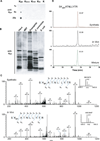
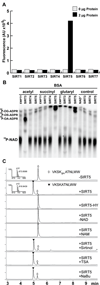
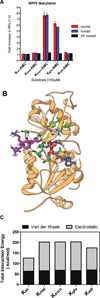
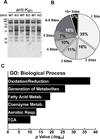
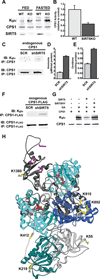
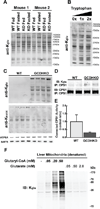
We report the identification and characterization of a five-carbon protein posttranslational modification (PTM) called lysine glutarylation (Kglu). This protein modification was detected by immunoblot and mass spectrometry (MS), and then comprehensively validated by chemical and biochemical methods. We demonstrated that the previously annotated deacetylase, sirtuin 5 (SIRT5), is a lysine deglutarylase. Proteome-wide analysis identified 683 Kglu sites in 191 proteins and showed that Kglu is highly enriched on metabolic enzymes and mitochondrial proteins. We validated carbamoyl phosphate synthase 1 (CPS1), the rate-limiting enzyme in urea cycle, as a glutarylated protein and demonstrated that CPS1 is targeted by SIRT5 for deglutarylation. We further showed that glutarylation suppresses CPS1 enzymatic activity in cell lines, mice, and a model of glutaric acidemia type I disease, the last of which has elevated glutaric acid and glutaryl-CoA. This study expands the landscape of lysine acyl modifications and increases our understanding of the deacylase SIRT5.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Berger SL. The complex language of chromatin regulation during transcription. Nature. 2007;447:407–412. - PubMed
-
- Chalkiadaki A, Guarente L. Sirtuins mediate mammalian metabolic responses to nutrient availability. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2012;8:287–296. - PubMed
-
- Chan CH, Ramirez-Montealegre D, Pearce DA. Altered arginine metabolism in the central nervous system (CNS) of the Cln3−/− mouse model of juvenile Batten disease. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2009;35:189–207. - PubMed
-
- Chen Y, Kwon SW, Kim SC, Zhao Y. Integrated approach for manual evaluation of peptides identified by searching protein sequence databases with tandem mass spectra. J Proteome Res. 2005;4:998–1005. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- T32 AG000114/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U54 RR020839/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R21 CA177925/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA160036/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- AA022146/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG045351/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM101171/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 5P30DK096493-02/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG013283/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30-AG-013283/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- F31 AG047696/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000430/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- CA059365-19/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK096493/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA059365/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- AG045351/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA160036/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM105933/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM105933/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- CA177925/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- RR020839/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020572/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 5T32GM007105-40/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA022146/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007105/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007315/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM101171/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

