Cellular profile of the dorsal raphe lateral wing sub-region: relationship to the lateral dorsal tegmental nucleus
- PMID: 24704911
- PMCID: PMC4065778
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jchemneu.2014.03.001
Cellular profile of the dorsal raphe lateral wing sub-region: relationship to the lateral dorsal tegmental nucleus
Abstract
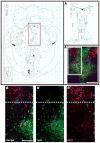
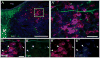
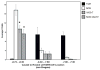
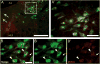
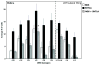
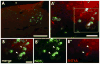
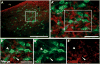
As one of the main serotonergic (5HT) projections to the forebrain, the dorsal raphe nucleus (DRN) has been implicated in disorders of anxiety and depression. Although the nucleus contains the densest population of 5HT neurons in the brain, at least 50% of cells within this structure are non-serotonergic, including a large population of nitric oxide synthase (NOS) containing neurons. The DRN has a unique topographical efferent organization and can also be divided into sub-regions based on rostro-caudal and medio-lateral dimensions. NOS is co-localized with 5HT in the midline DRN but NOS-positive cells in the lateral wing (LW) of the nucleus do not express 5HT. Interestingly, the NOS LW neuronal population is immediately rostral to and in line with the cholinergic lateral dorsal tegmental nucleus (LDT). We used immunohistochemical methods to investigate the potential serotonergic regulation of NOS LW neurons and also the association of this cell grouping to the LDT. Our results indicate that >75% of NOS LW neurons express the inhibitory 5HT1A receptor and are cholinergic (>90%). The findings suggest this assembly of cells is a rostral extension of the LDT, one that it is subject to regulation by 5HT release. As such the present study suggests a link between 5HT signaling, activation of cholinergic/NOS neurons, and the stress response including the pathophysiology underlying anxiety and depression.
Keywords: Acetylcholine; Dorsal raphe; Lateral dorsal tegmental nucleus; Nitric oxide synthase; Serotonin.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Abrams JK, et al. Serotonergic systems associated with arousal and vigilance behaviors following administration of anxiogenic drugs. Neuroscience. 2005;133:983–997. - PubMed
-
- Blier P, de Montigny C. Serotonin and drug-induced therapeutic responses in major depression, obsessive-compulsive and panic disorders. Neuropsychopharmacology. 1999;21:91S–98S. - PubMed
-
- Bonnavion P, et al. Heterogeneous distribution of the serotonin 5-HT(1A) receptor mRNA in chemically identified neurons of the mouse rostral brainstem: Implications for the role of serotonin in the regulation of wakefulness and REM sleep. J Comp Neurol. 2010;518:2744–2770. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

