MMP-7 is upregulated by COX-2 and promotes proliferation and invasion of lung adenocarcinoma cells
- PMID: 24704993
- PMCID: PMC3980206
- DOI: 10.4081/ejh.2014.2262
MMP-7 is upregulated by COX-2 and promotes proliferation and invasion of lung adenocarcinoma cells
Erratum in
-
Erratum - MMP-7 is upregulated by COX-2 and promotes proliferation and invasion of lung adenocarcinoma cells.Eur J Histochem. 2024 Jul 17;68(3):4109. doi: 10.4081/ejh.2024.4109. Eur J Histochem. 2024. PMID: 39015066 Free PMC article.
Abstract
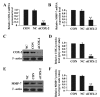
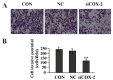
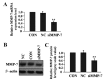
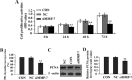
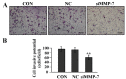
Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) have been implicated in a variety of pathophysiological conditions, of which MMP-7 is expressed by tumor cells of epithelial and mesenchymal origin. However, the function of MMP-7 in human lung adenocarcinoma (LAC) is unclear. In the present study the expression of MMP-7 in LAC was examined by immunohistochemical assay using a tissue microarray procedure. A loss-of-function experiment was performed to explore the effects and molecular mechanisms of lentiviral vector-mediated MMP-7 siRNA (siMMP-7) on cell proliferation and invasive potential in LAC A549 cells, measured by MTT and Transwell assays, respectively. It was found that, the expression of MMP-7 protein in LAC was significantly increased compared with that in adjacent non-cancerous tissues (ANCT) (76.0% vs 44.0%, P<0.001), and positively correlated with lymph node metastases of the tumor (P=0.014). Furthermore, targeted inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) by siRNA downregulated the expression of MMP-7 and inhibited invasion of LAC cells, and knockdown of MMP-7 suppressed tumor proliferation and invasion in LAC cells. Taken together, our findings indicate that increased expression of MMP-7 is associated with lymph node metastasis and upregulated by COX-2, and promotes the tumorigenesis of LAC, suggesting that MMP-7 may be a potential therapeutic target for the treatment of cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest disclosure: no conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Knockdown of PTTG1 inhibits the growth and invasion of lung adenocarcinoma cells through regulation of TGFB1/SMAD3 signaling.Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2015 Mar;28(1):45-52. doi: 10.1177/0306419015572073. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25816405
-
ZNF185 inhibits growth and invasion of lung adenocarcinoma cells through inhibition of the akt/gsk3β pathway.J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2016 Jul-Sep;30(3):683-691. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2016. PMID: 27655485
-
Knockdown of MMP12 inhibits the growth and invasion of lung adenocarcinoma cells.Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2015 Mar;28(1):77-84. doi: 10.1177/0394632015572557. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25816409
-
Knockdown of the inflammatory factor pentraxin-3 suppresses growth and invasion of lung adenocarcinoma through the AKT and NF-kappa B pathways.J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2014 Oct-Dec;28(4):649-57. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2014. PMID: 25620175
-
YES-associated protein 1 promotes adenocarcinoma growth and metastasis through activation of the receptor tyrosine kinase Axl.Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2012 Oct-Dec;25(4):989-1001. doi: 10.1177/039463201202500416. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 23298489
Cited by
-
A Comprehensive Pan-Cancer Analysis of the Tumorigenic Role of Matrix Metallopeptidase 7 (MMP7) Across Human Cancers.Front Oncol. 2022 Jun 17;12:916907. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.916907. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35785154 Free PMC article.
-
Is there still room for novelty, in histochemical papers?Eur J Histochem. 2016 Dec 16;60(4):2758. doi: 10.4081/ejh.2016.2758. Eur J Histochem. 2016. PMID: 28076939 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COX-2 overexpression and -8473 T/C polymorphism in 3' UTR in non-small cell lung cancer.Tumour Biol. 2014 Nov;35(11):11209-18. doi: 10.1007/s13277-014-2420-0. Epub 2014 Aug 12. Tumour Biol. 2014. PMID: 25113252
-
Histochemistry in biology and medicine: a message from the citing journals.Eur J Histochem. 2015 Dec 23;59(4):2610. doi: 10.4081/ejh.2015.2610. Eur J Histochem. 2015. PMID: 26708189 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Correlation and significance of COX-2, Ki67, VEGF and other immune indexes with the growth of malignant pulmonary nodules.J Cardiothorac Surg. 2022 Nov 16;17(1):290. doi: 10.1186/s13019-022-02039-7. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2022. PMID: 36384712 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin 2013;63:11-30 - PubMed
-
- William WN, Jr, Glisson BS. Novel strategies for the treatment of small-cell lung carcinoma. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2011;8:611-9 - PubMed
-
- Tajima Y, Yamazaki K, Makino R, Nishino N, Aoki S, Kato M, et al. Gastric and intestinal phenotypic marker expression in early differentiated-type tumors of the stomach: clinicopathologic significance and genetic background. Clin Cancer Res 2006;12:6469-79 - PubMed
-
- Leinonen T, Pirinen R, Böhm J, Johansson R, Ropponen K, Kosma VM. Expression of matrix metalloproteinases 7 and 9 in non-small cell lung cancer. Relation to clinico-pathological factors, betacatenin and prognosis. Lung Cancer 2006;51:313-21 - PubMed
-
- Kren L, Goncharuk VN, Krenová Z, Stratil D, Hermanová M, Skricková J, et al. Expression of matrix metalloproteinases 3, 10 and 11 (stromelysins 1, 2 and 3) and matrix metalloproteinase 7 (matrilysin) by cancer cells in non-small cell lung neoplasms. Clinicopathologic studies. Cesk Patol 2006;42:16-9 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

