RNAi in Arthropods: Insight into the Machinery and Applications for Understanding the Pathogen-Vector Interface
- PMID: 24705082
- PMCID: PMC3899984
- DOI: 10.3390/genes3040702
RNAi in Arthropods: Insight into the Machinery and Applications for Understanding the Pathogen-Vector Interface
Abstract
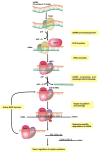
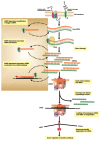
The availability of genome sequencing data in combination with knowledge of expressed genes via transcriptome and proteome data has greatly advanced our understanding of arthropod vectors of disease. Not only have we gained insight into vector biology, but also into their respective vector-pathogen interactions. By combining the strengths of postgenomic databases and reverse genetic approaches such as RNAi, the numbers of available drug and vaccine targets, as well as number of transgenes for subsequent transgenic or paratransgenic approaches, have expanded. These are now paving the way for in-field control strategies of vectors and their pathogens. Basic scientific questions, such as understanding the basic components of the vector RNAi machinery, is vital, as this allows for the transfer of basic RNAi machinery components into RNAi-deficient vectors, thereby expanding the genetic toolbox of these RNAi-deficient vectors and pathogens. In this review, we focus on the current knowledge of arthropod vector RNAi machinery and the impact of RNAi on understanding vector biology and vector-pathogen interactions for which vector genomic data is available on VectorBase.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of RNA interference (RNAi) in arbovirus-vector interactions.Viruses. 2015 Feb 17;7(2):820-43. doi: 10.3390/v7020820. Viruses. 2015. PMID: 25690800 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Update on the proteomics of major arthropod vectors of human and animal pathogens.Proteomics. 2012 Dec;12(23-24):3510-23. doi: 10.1002/pmic.201200300. Epub 2012 Nov 12. Proteomics. 2012. PMID: 23077092 Review.
-
RNA Interference in Insect Vectors for Plant Viruses.Viruses. 2016 Dec 12;8(12):329. doi: 10.3390/v8120329. Viruses. 2016. PMID: 27973446 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genomic resources for invertebrate vectors of human pathogens, and the role of VectorBase.Infect Genet Evol. 2009 May;9(3):308-13. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2007.12.007. Epub 2008 Jan 3. Infect Genet Evol. 2009. PMID: 18262474 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Arthropod-borne pathogens of dogs and cats: From pathways and times of transmission to disease control.Vet Parasitol. 2018 Feb 15;251:68-77. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2017.12.021. Epub 2017 Dec 27. Vet Parasitol. 2018. PMID: 29426479 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification and RNAi Profile of a Novel Iflavirus Infecting Senegalese Aedes vexans arabiensis Mosquitoes.Viruses. 2020 Apr 14;12(4):440. doi: 10.3390/v12040440. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32295109 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclease Tudor-SN Is Involved in Tick dsRNA-Mediated RNA Interference and Feeding but Not in Defense against Flaviviral or Anaplasma phagocytophilum Rickettsial Infection.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 17;10(7):e0133038. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0133038. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26186700 Free PMC article.
-
Prospects and challenges of CRISPR/Cas genome editing for the study and control of neglected vector-borne nematode diseases.FEBS J. 2016 Sep;283(17):3204-21. doi: 10.1111/febs.13781. Epub 2016 Jul 11. FEBS J. 2016. PMID: 27300487 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current Scenario of Exogenously Induced RNAi for Lepidopteran Agricultural Pest Control: From dsRNA Design to Topical Application.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 13;23(24):15836. doi: 10.3390/ijms232415836. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36555476 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lucilia cuprina genome unlocks parasitic fly biology to underpin future interventions.Nat Commun. 2015 Jun 25;6:7344. doi: 10.1038/ncomms8344. Nat Commun. 2015. PMID: 26108605 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Severson D.W., Behura S.K. Mosquito genomics: progress and challenges. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2012;57:143–166. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

