Efficacy and safety of radotinib in chronic phase chronic myeloid leukemia patients with resistance or intolerance to BCR-ABL1 tyrosine kinase inhibitors
- PMID: 24705186
- PMCID: PMC4077080
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2013.096776
Efficacy and safety of radotinib in chronic phase chronic myeloid leukemia patients with resistance or intolerance to BCR-ABL1 tyrosine kinase inhibitors
Abstract
Radotinib (IY5511HCL), a novel and selective BCR-ABL1 tyrosine kinase inhibitor, has shown pre-clinical and phase I activity and safety in chronic myeloid leukemia. This phase II study investigated the efficacy and safety of radotinib in Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic phase-chronic myeloid leukemia patients with resistance and/or intolerance to BCR-ABL1 tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Patients received radotinib 400 mg twice daily for 12 cycles based on results from the phase I trial. The primary end point was rate of major cytogenetic response by 12 months. A total of 77 patients were enrolled. Major cytogenetic response was achieved in 50 (65%; cumulative 75%) patients, including 36 (47%) patients with complete cytogenetic response by 12 months. Median time to major cytogenetic response and complete cytogenetic response were 85 days and 256 days, respectively. Major cytogenetic response and complete cytogenetic response rates were similar between imatinib-resistant and imatinib-intolerant patients, but were higher in patients without BCR-ABL1 mutations. Overall and progression-free survival rates at 12 months were 96.1% and 86.3%, respectively. All newly-occurring or worsening grade 3/4 hematologic abnormalities included thrombocytopenia (24.7%) and anemia (5.2%); grade 3/4 drug-related non-hematologic adverse events included fatigue (3.9%), asthenia (3.9%), and nausea (2.6%). The most common biochemistry abnormality was hyperbilirubinemia (grade 3/4 23.4%), and 12 of 18 cases were managed with dose modification. Study findings suggest radotinib is effective and well tolerated in chronic phase-chronic myeloid leukemia patients with resistance and/or intolerance to BCR-ABL1 tyrosine kinase inhibitors and may represent a promising alternative for these patients. (clinicaltrials.gov identifier: 01602952).
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01602952.
Copyright© Ferrata Storti Foundation.
Figures
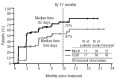

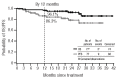
Comment in
-
Radotinib in the treatment of chronic phase chronic myeloid leukemia patients.Haematologica. 2015 Jan;100(1):e39. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2014.117846. Haematologica. 2015. PMID: 25552681 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Comment on "efficacy and safety of radotinib in chronic phase chronic myeloid leukemia patients with resistance or intolerance to BCR-ABL1 tyrosine kinase inhibitors".Haematologica. 2015 Mar;100(3):e120-1. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2014.123232. Haematologica. 2015. PMID: 25740109 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Faderl S, Talpaz M, Estrov Z, O’Brien S, Kurzrock R, Kantarjian HM. The biology of chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 1999;341(3):164–72 - PubMed
-
- Deininger MWN, Goldman JM, Melo JV. The molecular biology of chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2000;96(10):3343–56 - PubMed
-
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology™. Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia. Version 3. 2013. Updated 2013. Available from: http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/PDF/cml.pdf
-
- Hochhaus A, O’Brien SG, Guilhot F, Druker BJ, Branford S, Foroni L, et al. Six-year follow-up of patients receiving imatinib for the first-line treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. 2009;23(6):1054–61 - PubMed
-
- Gorre ME, Mohammed M, Ellwood K, Hsu N, Paquette R, Rao PN, et al. Clinical resistance to STI-571 cancer therapy caused by BCR-ABL gene mutation or amplification. Science. 2001;293(5531):876–80 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

