Circulating exosomal microRNAs as biomarkers of colon cancer
- PMID: 24705249
- PMCID: PMC3976275
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0092921
Circulating exosomal microRNAs as biomarkers of colon cancer
Abstract
Purpose: Exosomal microRNAs (miRNAs) have been attracting major interest as potential diagnostic biomarkers of cancer. The aim of this study was to characterize the miRNA profiles of serum exosomes and to identify those that are altered in colorectal cancer (CRC). To evaluate their use as diagnostic biomarkers, the relationship between specific exosomal miRNA levels and pathological changes of patients, including disease stage and tumor resection, was examined.
Experimental design: Microarray analyses of miRNAs in exosome-enriched fractions of serum samples from 88 primary CRC patients and 11 healthy controls were performed. The expression levels of miRNAs in the culture medium of five colon cancer cell lines were also compared with those in the culture medium of a normal colon-derived cell line. The expression profiles of miRNAs that were differentially expressed between CRC and control sample sets were verified using 29 paired samples from post-tumor resection patients. The sensitivities of selected miRNAs as biomarkers of CRC were evaluated and compared with those of known tumor markers (CA19-9 and CEA) using a receiver operating characteristic analysis. The expression levels of selected miRNAs were also validated by quantitative real-time RT-PCR analyses of an independent set of 13 CRC patients.
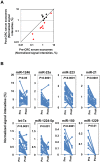
Results: The serum exosomal levels of seven miRNAs (let-7a, miR-1229, miR-1246, miR-150, miR-21, miR-223, and miR-23a) were significantly higher in primary CRC patients, even those with early stage disease, than in healthy controls, and were significantly down-regulated after surgical resection of tumors. These miRNAs were also secreted at significantly higher levels by colon cancer cell lines than by a normal colon-derived cell line. The high sensitivities of the seven selected exosomal miRNAs were confirmed by a receiver operating characteristic analysis.
Conclusion: Exosomal miRNA signatures appear to mirror pathological changes of CRC patients and several miRNAs are promising biomarkers for non-invasive diagnosis of the disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Jemal A, Bray F (2011) Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, et al (2011) Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 61: 69–90. - PubMed
-
- Atkin WS, Edwards R, Kralj-Hans I, Wooldrage K, Hart AR, et al. (2010) Once-only flexible sigmoidoscopy screening in prevention of colorectal cancer: a multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet 375: 1624–1633. - PubMed
-
- Bretthauer M (2010) Evidence for colorectal cancer screening. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 24: 417–425. - PubMed
-
- Locker GY, Hamilton S, Harris J, Jessup JM, Kemeny N, et al. (2006) ASCO 2006 update of recommendations for the use of tumor markers in gastrointestinal cancer. J Clin Oncol 24: 5313–5327. - PubMed
-
- Esquela-Kerscher A, Slack FJ (2006) Oncomirs - microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 6: 259–269. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

