The genetics of diabetic nephropathy
- PMID: 24705265
- PMCID: PMC3927570
- DOI: 10.3390/genes4040596
The genetics of diabetic nephropathy
Abstract
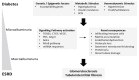
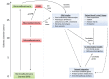
Up to 40% of patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes will develop diabetic nephropathy (DN), resulting in chronic kidney disease and potential organ failure. There is evidence for a heritable genetic susceptibility to DN, but despite intensive research efforts the causative genes remain elusive. Recently, genome-wide association studies have discovered several novel genetic variants associated with DN. The identification of such variants may potentially allow for early identification of at risk patients. Here we review the current understanding of the key molecular mechanisms and genetic architecture of DN, and discuss the merits of employing an integrative approach to incorporate datasets from multiple sources (genetics, transcriptomics, epigenetic, proteomic) in order to fully elucidate the genetic elements contributing to this serious complication of diabetes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genetics and Epigenetics of Diabetic Nephropathy.Kidney Dis (Basel). 2015 May;1(1):42-51. doi: 10.1159/000381796. Epub 2015 Apr 16. Kidney Dis (Basel). 2015. PMID: 27536664 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetics of diabetic nephropathy: are there clues to the understanding of common kidney diseases?Nephron Clin Pract. 2009;112(4):c213-21. doi: 10.1159/000224787. Epub 2009 Jun 16. Nephron Clin Pract. 2009. PMID: 19546580 Review.
-
Human genetics of diabetic nephropathy.Ren Fail. 2015 Apr;37(3):363-71. doi: 10.3109/0886022X.2014.1000801. Epub 2015 Jan 16. Ren Fail. 2015. PMID: 25594612 Review.
-
[Advances of genetics in diabetic nephropathy].Yi Chuan. 2012 Dec;34(12):1537-44. doi: 10.3724/sp.j.1005.2012.01537. Yi Chuan. 2012. PMID: 23262100 Review. Chinese.
-
Susceptibility gene search for nephropathy and related traits in Mexican-Americans.Mol Biol Rep. 2013 Oct;40(10):5769-79. doi: 10.1007/s11033-013-2680-6. Epub 2013 Sep 22. Mol Biol Rep. 2013. PMID: 24057238 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Association of the interaction between interleukin-1β gene polymorphism and smoking status with the diabetic nephropathy risk in a Chinese Han population.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2025 Mar 25;17(1):101. doi: 10.1186/s13098-025-01667-y. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2025. PMID: 40128741 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic risk score for risk prediction of diabetic nephropathy in Han Chinese type 2 diabetes patients.Sci Rep. 2019 Dec 27;9(1):19897. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-56400-3. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31882689 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The rs3844492/ARHGAP22 and rs741301/ELMO1 polymorphisms are associated with changes in laboratory markers of renal damage among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.Arch Endocrinol Metab. 2025 Apr 23;69(2):e240167. doi: 10.20945/2359-4292-2024-0167. Arch Endocrinol Metab. 2025. PMID: 40271977 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-30e-5p and MiR-15a-5p Expressions in Plasma and Urine of Type 1 Diabetic Patients With Diabetic Kidney Disease.Front Genet. 2019 Jun 12;10:563. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.00563. eCollection 2019. Front Genet. 2019. PMID: 31249597 Free PMC article.
-
Rutin suppresses high glucose-induced ACTA2 and p38 protein expression in diabetic nephropathy.Exp Ther Med. 2017 Jul;14(1):181-186. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.4509. Epub 2017 May 23. Exp Ther Med. 2017. PMID: 28672912 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Groop P.H., Thomas M.C., Moran J.L., Waden J., Thorn L.M., Makinen V.P., Rosengard-Barlund M., Saraheimo M., Hietala K., Heikkila O., et al. The presence and severity of chronic kidney disease predicts all-cause mortality in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes. 2009;58:1651–1658. doi: 10.2337/db08-1543. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Collins A.J., Foley R.N., Chavers B., Gilbertson D., Herzog C., Johansen K., Kasiske B., Kutner N., Liu J., St Peter W., et al. United States renal data system 2011 annual data report: Atlas of chronic kidney disease & end-stage renal disease in the United States. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2012;59:e1–e420. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2011.10.014. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

