Inhibition of fatty acid binding proteins elevates brain anandamide levels and produces analgesia
- PMID: 24705380
- PMCID: PMC3976407
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0094200
Inhibition of fatty acid binding proteins elevates brain anandamide levels and produces analgesia
Abstract
The endocannabinoid anandamide (AEA) is an antinociceptive lipid that is inactivated through cellular uptake and subsequent catabolism by fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH). Fatty acid binding proteins (FABPs) are intracellular carriers that deliver AEA and related N-acylethanolamines (NAEs) to FAAH for hydrolysis. The mammalian brain expresses three FABP subtypes: FABP3, FABP5, and FABP7. Recent work from our group has revealed that pharmacological inhibition of FABPs reduces inflammatory pain in mice. The goal of the current work was to explore the effects of FABP inhibition upon nociception in diverse models of pain. We developed inhibitors with differential affinities for FABPs to elucidate the subtype(s) that contributes to the antinociceptive effects of FABP inhibitors. Inhibition of FABPs reduced nociception associated with inflammatory, visceral, and neuropathic pain. The antinociceptive effects of FABP inhibitors mirrored their affinities for FABP5, while binding to FABP3 and FABP7 was not a predictor of in vivo efficacy. The antinociceptive effects of FABP inhibitors were mediated by cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1) and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARα) and FABP inhibition elevated brain levels of AEA, providing the first direct evidence that FABPs regulate brain endocannabinoid tone. These results highlight FABPs as novel targets for the development of analgesic and anti-inflammatory therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
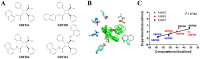
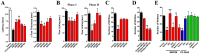
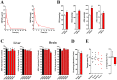

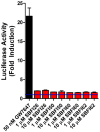
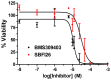
References
-
- De Leon M, Welcher AA, Nahin RH, Liu Y, Ruda MA, et al. (1996) Fatty acid binding protein is induced in neurons of the dorsal root ganglia after peripheral nerve injury. J Neurosci Res 44: 283–292. - PubMed
-
- Boneva NB, Mori Y, Kaplamadzhiev DB, Kikuchi H, Zhu H, et al. (2010) Differential expression of FABP 3, 5, 7 in infantile and adult monkey cerebellum. Neurosci Res 68: 94–102. - PubMed
-
- Boneva NB, Kaplamadzhiev DB, Sahara S, Kikuchi H, Pyko IV, et al. (2011) Expression of fatty acid-binding proteins in adult hippocampal neurogenic niche of postischemic monkeys. Hippocampus 21: 162–171. - PubMed
-
- Yamamoto T, Yamamoto A, Watanabe M, Matsuo T, Yamazaki N, et al. (2009) Classification of FABP isoforms and tissues based on quantitative evaluation of transcript levels of these isoforms in various rat tissues. Biotechnol Lett 31: 1695–1701. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

