Placotylene A, an inhibitor of the receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand-induced osteoclast differentiation, from a Korean sponge Placospongia sp
- PMID: 24705502
- PMCID: PMC4012465
- DOI: 10.3390/md12042054
Placotylene A, an inhibitor of the receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand-induced osteoclast differentiation, from a Korean sponge Placospongia sp
Abstract
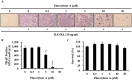
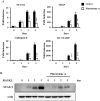
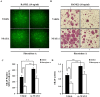
A new inhibitor, placotylene A (1), of the receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand (RANKL)-induced osteoclast differentiation, and a regioisomer of placotylene A, placotylene B (2), were isolated from a Korean marine sponge Placospongia sp. The chemical structures of placotylenes A and B were elucidated on the basis of 1D and 2D NMR, along with MS spectral analysis and revealed as an iodinated polyacetylene class of natural products. Placotylene A (1) displayed inhibitory activity against RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation at 10 μM while placotylene B (2) did not show any significant activity up to 100 μM, respectively.
Figures


References
-
- Gribble G.W. Natural organohalogens: A new frontier for medicinal agents? J. Chem. Educ. 2004;81:1441–1449. doi: 10.1021/ed081p1441. - DOI
-
- Faulkner D.J. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 1997;14:259–302.
-
- Lerch M.L., Harper M.K., Faulkner D.J. Brominated polyacetylenes from the Philippines sponge Diplastrella sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2003;66:667–670. - PubMed
-
- Bourguet-Kondracki M.L., Rakotoatisoa M.T., Martin M.T., Guyot M. Brominated polyacetylenic acids from the marine sponge Xestospongia muta: Inhibitors of HIV protease. Tetrahedron Lett. 1992;33:225–226.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

