Are there risk factors for complications of perforator-based propeller flaps for lower-extremity reconstruction?
- PMID: 24706021
- PMCID: PMC4048426
- DOI: 10.1007/s11999-014-3537-6
Are there risk factors for complications of perforator-based propeller flaps for lower-extremity reconstruction?
Abstract
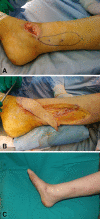
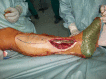
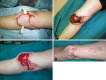
Background: Conventional pedicled flaps for soft tissue reconstruction of lower extremities have shortcomings, including donor-site morbidity, restricted arc of rotation, and poor cosmetic results. Propeller flaps offer several potential advantages, including no need for microvascular anastomosis and low impact on donor sites, but their drawbacks have not been fully characterized.
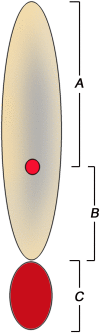
Questions/purposes: We assessed (1) frequency and types of complications after perforator-based propeller flap reconstruction in the lower extremity and (2) association of complications with arc of rotation, flap dimensions, and other potential risk factors.
Methods: From 2007 to 2012, 74 patients (44 males, 30 females), 14 to 87 years old, underwent soft tissue reconstruction of the lower extremities with propeller flaps. General indications for this flap were wounds and small- and medium-sized defects located in distal areas of the lower extremity, not suitable for coverage with myocutaneous or muscle pedicled flaps. This group represented 26% (74 of 283) of patients treated with vascularized coverage procedures for soft tissue defects in the lower limb during the study period. Minimum followup was 1 year (mean, 3 years; range, 1-7 years); eight patients (11%) were lost to followup before 1 year. Complications and potential risk factors, including arc of rotation, flap dimensions, age, sex, defect etiology, smoking, diabetes, and peripheral vascular disease, were recorded based on chart review.
Results: Twenty-eight of 66 flaps (42%) had complications. Venous congestion (11 of 66, 17%) and superficial necrosis (seven of 66, 11%) occurred most frequently. Eighteen of the 28 complications (64%) healed with no further treatment; eight patients (29%) underwent skin grafting, and one patient each experienced total flap failure (2%) and partial flap failure (2%). In those patients, a free anterolateral thigh flap was used as the salvage procedure. No correlations were found between complications and any potential risk factor.
Conclusions: We were not able to identify any specific risk factors related to complications, and future multicenter studies will be necessary to determine which patients or wounds are at risk of complications. Propeller flaps had a low failure rate and risk of secondary surgery. These flaps are particularly useful for covering small- and medium-sized defects in the distal leg and Achilles tendon region and are a reliable and effective alternative to free flaps.
Level of evidence: Level IV, therapeutic study. See the Instructions for Authors for a complete description of levels of evidence.
Figures



Similar articles
-
[Application of perforator propeller flap sequential transfer technique in repair of soft tissue defect of distal lower extremity].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2022 Apr 15;36(4):451-455. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.202111047. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35426285 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Institutional Experience and Orthoplastic Collaboration Associated with Improved Flap-based Limb Salvage Outcomes.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2021 Nov 1;479(11):2388-2396. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000001925. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2021. PMID: 34398852 Free PMC article.
-
Reconstruction of soft tissue defects in the extremities with a pedicled perforator flap: series of 25 patients.J Plast Surg Hand Surg. 2012 Feb;46(1):32-6. doi: 10.3109/2000656X.2011.634562. J Plast Surg Hand Surg. 2012. PMID: 22455574
-
One-stage reconstruction of composite bone and soft-tissue defects in traumatic lower extremities.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2004 Nov;114(6):1457-66. doi: 10.1097/01.prs.0000138811.88807.65. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2004. PMID: 15509933 Review.
-
Pedicled-perforator (propeller) flaps in lower extremity defects: a systematic review.J Reconstr Microsurg. 2012 Nov;28(9):595-601. doi: 10.1055/s-0032-1315786. Epub 2012 Jun 19. J Reconstr Microsurg. 2012. PMID: 22715046
Cited by
-
A Review of Pedicled Perforator Flaps for Reconstruction of the Soft Tissue Defects of the Leg and Foot.Indian J Plast Surg. 2019 Jan;52(1):26-36. doi: 10.1055/s-0039-1688103. Epub 2019 May 2. Indian J Plast Surg. 2019. PMID: 31456610 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Best Local Flaps for Lower Extremity Reconstruction.Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2020 Apr 30;8(4):e2774. doi: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000002774. eCollection 2020 Apr. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2020. PMID: 32440438 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reconstruction Using Perforator Propeller Flaps After Malignant Melanoma Resection of the Lower Extremity.Plast Surg (Oakv). 2024 May;32(2):276-282. doi: 10.1177/22925503221116279. Epub 2022 Aug 1. Plast Surg (Oakv). 2024. PMID: 38681257 Free PMC article.
-
The Microvascular Peroneal Artery Perforator Flap as a "Lifeboat" for Pedicled Flaps.Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2019 Sep 30;7(9):e2396. doi: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000002396. eCollection 2019 Sep. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2019. PMID: 31942377 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of pedicled flaps for type IIIB open fractures of the tibia at a tertiary care center.Arch Plast Surg. 2021 Jul;48(4):417-426. doi: 10.5999/aps.2020.02089. Epub 2021 Jul 15. Arch Plast Surg. 2021. PMID: 34352955 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

