Treatment patterns and clinical outcomes for patients with de novo versus recurrent HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer
- PMID: 24706168
- PMCID: PMC4031392
- DOI: 10.1007/s10549-014-2916-8
Treatment patterns and clinical outcomes for patients with de novo versus recurrent HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer
Abstract
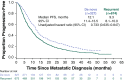
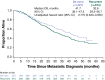
Improvements in screening and adjuvant therapy for breast cancer are associated with decreased recurrence, which may have the effect of increasing the proportion of patients presenting with first-line de novo versus recurrent metastatic breast cancer (MBC). Here, we describe and compare patients with de novo versus recurrent human epidermal growth factor 2 (HER2)-positive MBC. registHER was a prospective observational cohort study (late 2003-early 2006) of 1,023 patients with HER2-positive MBC. Baseline characteristics, treatment patterns, and clinical outcomes were examined in patients with newly diagnosed de novo (n = 327) compared with recurrent HER2-positive MBC after prior treatment for early-stage disease (n = 674). Patients with de novo HER2-positive MBC were less likely to have lung metastases, more likely to have lymph node, bone, and/or liver metastases and >4 sites of metastases and more likely to receive combined or concurrent chemotherapy and hormonal therapy with or without trastuzumab than those with recurrent HER2-positive MBC. Median follow-up was 29 months. Median progression-free survival was 12.1 versus 9.3 months [hazard ratio = 0.716 (95 % confidence interval (CI) 0.617-0.831)], and overall survival was 41.7 versus 32.8 months [hazard ratio = 0.766 (95 % CI 0.633-0.928)] for patients with de novo versus recurrent HER2-positive MBC, respectively. Patients with recurrent HER2-positive MBC had similar outcomes regardless of whether they received prior adjuvant therapy, excluding hormonal therapy. Despite presenting with more advanced-stage disease and higher tumor burdens, patients with de novo HER2-positive MBC have more favorable clinical outcomes than those with recurrent HER2-positive MBC. These differences may be due to effects of prior drug exposure and could have implications for designing and interpreting clinical trials.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Clinical outcome in women with HER2-positive de novo or recurring stage IV breast cancer receiving trastuzumab-based therapy.Breast. 2014 Feb;23(1):44-9. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2013.10.005. Epub 2013 Nov 7. Breast. 2014. PMID: 24210572
-
De Novo Versus Recurrent HER2-Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer: Patient Characteristics, Treatment, and Survival from the SystHERs Registry.Oncologist. 2020 Feb;25(2):e214-e222. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2019-0446. Epub 2019 Oct 14. Oncologist. 2020. PMID: 32043771 Free PMC article.
-
Patterns of Care and Clinical Outcomes of HER2-positive Metastatic Breast Cancer Patients With Newly Diagnosed Stage IV or Recurrent Disease Undergoing First-line Trastuzumab-based Therapy: A Multicenter Retrospective Cohort Study.Clin Breast Cancer. 2017 Dec;17(8):601-610.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.clbc.2017.04.002. Epub 2017 Apr 11. Clin Breast Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28479052
-
Emerging approaches for treating HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer beyond trastuzumab.Ann Oncol. 2013 Oct;24(10):2492-2500. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdt217. Epub 2013 Jul 4. Ann Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23827380 Review.
-
Trastuzumab as first-line therapy in HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer patients.Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2012 Nov;12(11):1391-405. doi: 10.1586/era.12.107. Epub 2012 Oct 16. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2012. PMID: 23072512 Review.
Cited by
-
Pattern of metastasis and outcome in patients with breast cancer.Clin Exp Metastasis. 2015 Feb;32(2):125-33. doi: 10.1007/s10585-015-9697-2. Epub 2015 Jan 29. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2015. PMID: 25630269
-
Aggressive local therapy for de novo metastatic breast cancer: Challenges and updates (Review).Oncol Rep. 2023 Sep;50(3):163. doi: 10.3892/or.2023.8600. Epub 2023 Jul 14. Oncol Rep. 2023. PMID: 37449542 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Health-related quality of life and work productivity in UK patients with HER2-positive breast cancer: a cross-sectional study evaluating the relationships between disease and treatment stage.Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2020 Nov 2;18(1):353. doi: 10.1186/s12955-020-01603-w. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2020. PMID: 33138835 Free PMC article.
-
Survival outcomes for Australian women receiving trastuzumab for HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer following (neo)adjuvant trastuzumab: a national population-based observational study (2006-2014).Br J Cancer. 2018 Feb 6;118(3):441-447. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2017.405. Epub 2017 Nov 14. Br J Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29136405 Free PMC article.
-
Economic evaluation of adjuvant trastuzumab emtansine in patients with HER2-positive early breast cancer and residual invasive disease after neoadjuvant taxane and trastuzumab-based treatment in Canada.Curr Oncol. 2020 Dec;27(6):e578-e589. doi: 10.3747/co.27.6517. Epub 2020 Dec 1. Curr Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33380873 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berry DA, Cronin KA, Plevritis SK, Fryback DG, Clarke L, Zelen M, Mandelblatt JS, Yakovlev AY, Habbema JD, Feuer EJ, Cancer Intervention and Surveillance Modeling Network (CISNET) Collaborators Effect of screening and adjuvant therapy on mortality from breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:1784–1792. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa050518. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Piccart-Gebhart MJ, Procter M, Leyland-Jones B, Goldhirsch A, Untch M, Smith I, Gianni L, Baselga J, Bell R, Jackisch C, Cameron D, Dowsett M, Barrios CH, Steger G, Huang CS, Andersson M, Inbar M, Lichinitser M, Láng I, Nitz U, Iwata H, Thomssen C, Lohrisch C, Suter TM, Rüschoff J, Suto T, Greatorex V, Ward C, Straehle C, McFadden E, Dolci MS, Gelber RD, Herceptin Adjuvant (HERA) Trial Study Team Trastuzumab after adjuvant chemotherapy in HER2-positive breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:1659–1672. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa052306. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Romond EH, Perez EA, Bryant J, Suman VJ, Geyer CE, Jr, Davidson NE, Tan-Chiu E, Martino S, Paik S, Kaufman PA, Swain SM, Pisansky TM, Fehrenbacher L, Kutteh LA, Vogel VG, Visscher DW, Yothers G, Jenkins RB, Brown AM, Dakhil SR, Mamounas EP, Lingle WL, Klein PM, Ingle JN, Wolmark N. Trastuzumab plus adjuvant chemotherapy for operable HER2-positive breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:1673–1684. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa052122. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Slamon D, Eiermann W, Robert N, Pienkowski T, Martin M, Press M, Mackey J, Glaspy J, Chan A, Pawlicki M, Pinter T, Valero V, Liu M-C, Sauter G, von Minckwitz G, Visco F, Bee V, Buyse M, Bendahmane B, Tabah-Fisch I, Lindsay M, Riva A, Crown J, Breast Cancer International Research Group Adjuvant trastuzumab in HER2-positive breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:1273–1283. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0910383. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

