Novel TUBB4A mutations and expansion of the neuroimaging phenotype of hypomyelination with atrophy of the basal ganglia and cerebellum (H-ABC)
- PMID: 24706558
- PMCID: PMC10506160
- DOI: 10.1002/ajmg.a.36526
Novel TUBB4A mutations and expansion of the neuroimaging phenotype of hypomyelination with atrophy of the basal ganglia and cerebellum (H-ABC)
Abstract
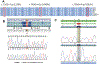
Hypomyelination with atrophy of the basal ganglia and cerebellum (H-ABC) has recently been associated with a single heterozygous p.D249N mutation in TUBB4A. We describe two novel mutations in this gene. A p.C239F mutation was found in one of the originally described H-ABC patients, for whom we provide follow-up 11 years after the original publication. The second novel mutation, p.R262H, was found in a patient with a typical clinical presentation for H-ABC, but with a novel neuroimaging phenotype, given the absence of atrophy of the putamen and caudate nucleus despite 7 years of follow-up. The recent recognition of TUBB4A mutations as the underlying etiology of H-ABC will likely lead to the identification of subtler clinical and neuroimaging presentations of this disorder, like in our third patient. Thus mutations in this gene should be suspected in any patient with hypomyelination, regardless of the long-term presence of neostriatal atrophy.
Keywords: TUBB4A; hypomyelination with atrophy of the basal ganglia and cerebellum; tubulin beta 4.
© 2014 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
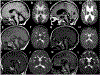
References
-
- Cushion TD, Dobyns WB, Mullins JG, Stoodley N, Chung SK, Fry AE, Hehr U, Gunny R, Aylsworth AS, Prabhakar P, Uyanik G, Rankin J, Rees MI, Pilz DT. 2013. Overlapping cortical malformations and mutations in TUBB2B and TUBA1A. Brain 136:536–548. - PubMed
-
- Hersheson J, Mencacci NE, Davis M, MacDonald N, Trabzuni D, Ryten M, Pittman A, Paudel R, Kara E, Fawcett K, Plagnol V, Bhatia KP, Medlar AJ, Stanescu HC, Hardy J, Kleta R, Wood NW, Houlden H. 2013. Mutations in the autoregulatory domain of β-tubulin 4a cause hereditary dystonia. Ann Neurol 73:546–553. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Leandro-García LJ, Leskela S, Landa I, Montero-Conde C, Lopez-Jimenez E, Leton R, Cascon A, Robledo M, Rodriguez-Antona C. 2010. Tumoral and tissue-specific expression of the major human beta-tubulin isotypes. Cytoskeleton 67:214–223. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

