Resolving nonstop translation complexes is a matter of life or death
- PMID: 24706739
- PMCID: PMC4054194
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.01490-14
Resolving nonstop translation complexes is a matter of life or death
Abstract
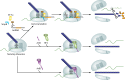
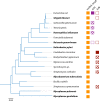
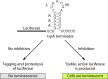
Problems during gene expression can result in a ribosome that has translated to the 3' end of an mRNA without terminating at a stop codon, forming a nonstop translation complex. The nonstop translation complex contains a ribosome with the mRNA and peptidyl-tRNA engaged, but because there is no codon in the A site, the ribosome cannot elongate or terminate the nascent chain. Recent work has illuminated the importance of resolving these nonstop complexes in bacteria. Transfer-messenger RNA (tmRNA)-SmpB specifically recognizes and resolves nonstop translation complexes in a reaction known as trans-translation. trans-Translation releases the ribosome and promotes degradation of the incomplete nascent polypeptide and problematic mRNA. tmRNA and SmpB have been found in all bacteria and are essential in some species. However, other bacteria can live without trans-translation because they have one of the alternative release factors, ArfA or ArfB. ArfA recruits RF2 to nonstop translation complexes to promote hydrolysis of the peptidyl-tRNAs. ArfB recognizes nonstop translation complexes in a manner similar to tmRNA-SmpB recognition and directly hydrolyzes the peptidyl-tRNAs to release the stalled ribosomes. Genetic studies indicate that most or all species require at least one mechanism to resolve nonstop translation complexes. Consistent with such a requirement, small molecules that inhibit resolution of nonstop translation complexes have broad-spectrum antibacterial activity. These results suggest that resolving nonstop translation complexes is a matter of life or death for bacteria.
Copyright © 2014, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

