Toll-like receptor-mediated down-regulation of the deubiquitinase cylindromatosis (CYLD) protects macrophages from necroptosis in wild-derived mice
- PMID: 24706750
- PMCID: PMC4022908
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.547547
Toll-like receptor-mediated down-regulation of the deubiquitinase cylindromatosis (CYLD) protects macrophages from necroptosis in wild-derived mice
Abstract
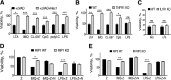
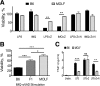
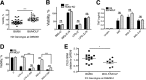
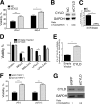
Pathogen recognition by the innate immune system initiates the production of proinflammatory cytokines but can also lead to programmed host cell death. Necroptosis, a caspase-independent cell death pathway, can contribute to the host defense against pathogens or cause damage to host tissues. Receptor-interacting protein (RIP1) is a serine/threonine kinase that integrates inflammatory and necroptotic responses. To investigate the mechanisms of RIP1-mediated activation of immune cells, we established a genetic screen on the basis of RIP1-mediated necroptosis in wild-derived MOLF/EiJ mice, which diverged from classical laboratory mice over a million years ago. When compared with C57BL/6, MOLF/EiJ macrophages were resistant to RIP1-mediated necroptosis induced by Toll-like receptors. Using a forward genetic approach in a backcross panel of mice, we identified cylindromatosis (CYLD), a deubiquitinase known to act directly on RIP1 and promote necroptosis in TNF receptor signaling, as the gene conferring the trait. We demonstrate that CYLD is required for Toll-like receptor-induced necroptosis and describe a novel mechanism by which CYLD is down-regulated at the transcriptional level in MOLF/EiJ macrophages to confer protection from necroptosis.
Keywords: Deubiquitination; Forward Genetic Mapping; Gene Regulation; Mouse Genetics; Necrosis (Necrotic Death); Toll-like Receptor (TLR); Wild-derived Mice.
© 2014 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures

Similar articles
-
CYLD deubiquitinates RIP1 in the TNFα-induced necrosome to facilitate kinase activation and programmed necrosis.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 2;8(10):e76841. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076841. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24098568 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of necroptotic cell death by viral activation of the RIG-I or STING pathway.Cell Death Differ. 2017 Apr;24(4):615-625. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2016.153. Epub 2017 Jan 6. Cell Death Differ. 2017. PMID: 28060376 Free PMC article.
-
CYLD Proteolysis Protects Macrophages from TNF-Mediated Auto-necroptosis Induced by LPS and Licensed by Type I IFN.Cell Rep. 2016 Jun 14;15(11):2449-61. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.05.032. Epub 2016 Jun 2. Cell Rep. 2016. PMID: 27264187 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms and pathways of innate immune activation and regulation in health and cancer.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2014;10(11):3270-85. doi: 10.4161/21645515.2014.979640. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2014. PMID: 25625930 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Necroptosis: an alternative cell death program defending against cancer.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Apr;1865(2):228-36. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2016.03.003. Epub 2016 Mar 8. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 26968619 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
CYLD, A20 and OTULIN deubiquitinases in NF-κB signaling and cell death: so similar, yet so different.Cell Death Differ. 2017 Jul;24(7):1172-1183. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2017.46. Epub 2017 Mar 31. Cell Death Differ. 2017. PMID: 28362430 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Smac-mimetics reduce numbers and viability of human osteoclasts.Cell Death Discov. 2021 Feb 19;7(1):36. doi: 10.1038/s41420-021-00415-1. Cell Death Discov. 2021. PMID: 33608503 Free PMC article.
-
Wild-derived mice: from genetic diversity to variation in immune responses.Mamm Genome. 2018 Aug;29(7-8):577-584. doi: 10.1007/s00335-018-9766-3. Epub 2018 Jul 28. Mamm Genome. 2018. PMID: 30056578 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The regulation of necroptosis by ubiquitylation.Apoptosis. 2022 Oct;27(9-10):668-684. doi: 10.1007/s10495-022-01755-8. Epub 2022 Aug 8. Apoptosis. 2022. PMID: 35939135 Review.
-
AKT and DUBs: a bidirectional relationship.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2025 Jul 7;30(1):77. doi: 10.1186/s11658-025-00753-3. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2025. PMID: 40624457 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Takeuchi O., Akira S. (2010) Pattern recognition receptors and inflammation. Cell 140, 805–820 - PubMed
-
- Duprez L., Wirawan E., Vanden Berghe T., Vandenabeele P. (2009) Major cell death pathways at a glance. Microbes Infect. 11, 1050–1062 - PubMed
-
- Duprez L., Takahashi N., Van Hauwermeiren F., Vandendriessche B., Goossens V., Vanden Berghe T., Declercq W., Libert C., Cauwels A., Vandenabeele P. (2011) RIP Kinase-dependent necrosis drives lethal systemic inflammatory response syndrome. Immunity 35, 908–918 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

