Interactions outside the proteinase-binding loop contribute significantly to the inhibition of activated coagulation factor XII by its canonical inhibitor from corn
- PMID: 24706752
- PMCID: PMC4022879
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.553735
Interactions outside the proteinase-binding loop contribute significantly to the inhibition of activated coagulation factor XII by its canonical inhibitor from corn
Abstract
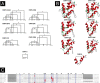
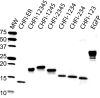
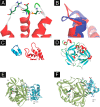
Activated factor XII (FXIIa) is selectively inhibited by corn Hageman factor inhibitor (CHFI) among other plasma proteases. CHFI is considered a canonical serine protease inhibitor that interacts with FXIIa through its protease-binding loop. Here we examined whether the protease-binding loop alone is sufficient for the selective inhibition of serine proteases or whether other regions of a canonical inhibitor are involved. Six CHFI mutants lacking different N- and C-terminal portions were generated. CHFI-234, which lacks the first and fifth disulfide bonds and 11 and 19 amino acid residues at the N and C termini, respectively, exhibited no significant changes in FXIIa inhibition (Ki = 3.2 ± 0.4 nm). CHFI-123, which lacks 34 amino acid residues at the C terminus and the fourth and fifth disulfide bridges, inhibited FXIIa with a Ki of 116 ± 16 nm. To exclude interactions outside the FXIIa active site, a synthetic cyclic peptide was tested. The peptide contained residues 20-45 (Protein Data Bank code 1BEA), and a C29D substitution was included to avoid unwanted disulfide bond formation between unpaired cysteines. Surprisingly, the isolated protease-binding loop failed to inhibit FXIIa but retained partial inhibition of trypsin (Ki = 11.7 ± 1.2 μm) and activated factor XI (Ki = 94 ± 11 μm). Full-length CHFI inhibited trypsin with a Ki of 1.3 ± 0.2 nm and activated factor XI with a Ki of 5.4 ± 0.2 μm. Our results suggest that the protease-binding loop is not sufficient for the interaction between FXIIa and CHFI; other regions of the inhibitor also contribute to specific inhibition.
Keywords: Blood Coagulation Factors; Enzyme Kinetics; Enzyme Mechanisms; Protease Inhibitor; Protein Expression; Protein-Protein Interactions; Serine Protease.
© 2014 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures


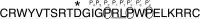
References
-
- Mahoney W. C., Hermodson M. A., Jones B., Powers D. D., Corfman R. S., Reeck G. R. (1984) Amino acid sequence and secondary structural analysis of the corn inhibitor of trypsin and activated Hageman factor. J. Biol. Chem. 259, 8412–8416 - PubMed
-
- Lei M. G., Reeck G. R. (1987) Resynthesis by factor XIIa of the trypsin-cleaved peptide bond in the corn protease inhibitor. Thromb. Res. 45, 87–94 - PubMed
-
- Hojima Y., Pierce J. V., Pisano J. J. (1980) Hageman factor fragment inhibitor in corn seeds: purification and characterization. Thromb. Res. 20, 149–162 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

