Regional brain responses associated with drinking water during thirst and after its satiation
- PMID: 24706817
- PMCID: PMC3986125
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1403382111
Regional brain responses associated with drinking water during thirst and after its satiation
Abstract
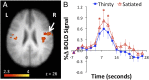
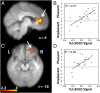
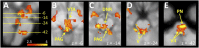
The instinct of thirst was a cardinal element in the successful colonization by vertebrates of the dry land of the planet, which began in the Ordovician period about 400 million y ago. It is a commonplace experience in humans that drinking water in response to thirst following fluid loss is a pleasant experience. However, continuing to drink water once thirst has been satiated becomes unpleasant and, eventually, quite aversive. Functional MRI experiments reported here show pleasantness of drinking is associated with activation in the anterior cingulate cortex (Brodmann area 32) and the orbitofrontal cortex. The unpleasantness and aversion of overdrinking is associated with activation in the midcingulate cortex, insula, amygdala, and periaqueductal gray. Drinking activations in the putamen and cerebellum also correlated with the unpleasantness of water, and the motor cortex showed increased activation during overdrinking compared with drinking during thirst. These activations in motor regions may possibly reflect volitional effort to conduct compliant drinking in the face of regulatory mechanisms inhibiting intake. The results suggestive of a specific inhibitory system in the control of drinking are unique.
Keywords: fMRI; swallowing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Denton D. The Hunger for Salt. An Anthropological, Physiological and Medical Analysis. Heidelberg: Springer; 1982.
-
- Fitzsimons JT. The Physiology of Thirst. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge Univ Press; 1972.
-
- Tinbergen N. The Study of Instinct. Oxford, UK: Clarendon; 1958.
-
- Wolf AV. Thirst. Physiology of the Urge to Drink and Problems of Water Lack. Springfield, IL: Charles C. Thomas; 1958.
-
- Adolph EF. Physiology of Man in the Desert. New York: Interscience; 1947.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

