The effect of a short-term high-intensity circuit training program on work capacity, body composition, and blood profiles in sedentary obese men: a pilot study
- PMID: 24707476
- PMCID: PMC3953517
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/191797
The effect of a short-term high-intensity circuit training program on work capacity, body composition, and blood profiles in sedentary obese men: a pilot study
Abstract
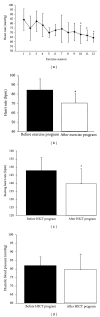
The objective of this study was to determine how a high-intensity circuit-training (HICT) program affects key physiological health markers in sedentary obese men. Eight obese (body fat percentage >26%) males completed a four-week HICT program, consisting of three 30-minute exercise sessions per week, for a total of 6 hours of exercise. Participants' heart rate (HR), blood pressure (BP), rating of perceived exertion, total work (TW), and time to completion were measured each exercise session, body composition was measured before and after HICT, and fasting blood samples were measured before throughout, and after HICT program. Blood sample measurements included total cholesterol, triacylglycerides, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, glucose, and insulin. Data were analyzed by paired t-tests and one-way ANOVA with repeated measures. Statistical significance was set to P < 0.05. Data analyses revealed significant (P < 0.05) improvements in resting HR (16% decrease), systolic BP (5.5% decrease), TW (50.7%), fat tissue percentage (3.6%), lean muscle tissue percentage (2%), cholesterol (13%), triacylglycerol (37%), and insulin (18%) levels from before to after HICT program. Overall, sedentary obese males experienced a significant improvement in biochemical, physical, and body composition characteristics from a HICT program that was only 6 hours of the total exercise.
Figures


References
-
- Church T. Exercise in obesity, metabolic syndrome, and diabetes. Progress in Cardiovascular Diseases. 2011;53(6):412–418. - PubMed
-
- Durstine JL, Moore GE, Painter PL, Roberts SO. Exercise Management for Persons with Chronic Diseases and Disabilites. 3rd edition. Human Kinetics; 2009.
-
- Jakicic JM, Marcus BH, Gallagher KI, Napolitano M, Lang W. Effect of exercise duration and intensity on weight loss in overweight, sedentary women: a randomized trial. Journal of the American Medical Association. 2003;290(10):1323–1330. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

