Slit2N and Robo4 regulate lymphangiogenesis through the VEGF-C/VEGFR-3 pathway
- PMID: 24708522
- PMCID: PMC4122147
- DOI: 10.1186/1478-811X-12-25
Slit2N and Robo4 regulate lymphangiogenesis through the VEGF-C/VEGFR-3 pathway
Abstract
Background: Signaling through vascular endothelial growth factor C (VEGF–C) and VEGF receptor 3 (VEGFR-3) plays a central role in lymphangiogenesis and the metastasis of several cancers via the lymphatics. Recently, the Slit2/Robo4 pathway has been recognized as a modulator of vascular permeability and integrity. Signaling via the Robo receptor inhibits VEGF-mediated effects; however, its effects on lymphatic endothelial cell function have not been well characterized.
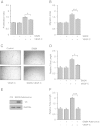
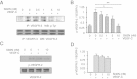
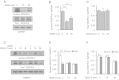
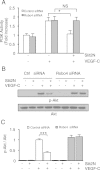
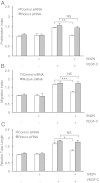
Results: We found that pretreatment with Slit2N, an active fragment of Slit2, inhibited VEGF-C-mediated lung-derived lymphatic endothelial cell (L-LEC) proliferation, migration, and in vitro tube formation. Slit2N induced the internalization of VEGFR-3, which blocked its activation, and inhibited the activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway by VEGF-C in L-LECs. Moreover, we found that inhibition of VEGF-C-induced effects by Slit2N was Robo4-dependent.
Conclusion: These results indicate that Slit2N/Robo4 modulates several key cellular functions, which contribute to lymphangiogenesis, and identify this ligand-receptor pair as a potential therapeutic target to inhibit lymphatic metastasis of VEGF-C-overexpressing cancers and manage lymphatic dysfunctions characterized by VEGF-C/VEGFR-3 activation.
Figures


References
-
- Bahram F, Claesson-Welsh L. VEGF-mediated signal transduction in lymphatic endothelial cells. Pathophysiology: the official journal of the International Society for Pathophysiology/ISP. 2010;17:253–261. - PubMed
-
- Salameh A, Galvagni F, Bardelli M, Bussolino F, Oliviero S. Direct recruitment of CRK and GRB2 to VEGFR-3 induces proliferation, migration, and survival of endothelial cells through the activation of ERK, AKT, and JNK pathways. Blood. 2005;106:3423–3431. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-04-1388. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

