Bortezomib in late antibody-mediated kidney transplant rejection (BORTEJECT Study): study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 24708575
- PMCID: PMC4014747
- DOI: 10.1186/1745-6215-15-107
Bortezomib in late antibody-mediated kidney transplant rejection (BORTEJECT Study): study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Despite major advances in transplant medicine, improvements in long-term kidney allograft survival have not been commensurate with those observed shortly after transplantation. The formation of donor-specific antibodies (DSA) and ongoing antibody-mediated rejection (AMR) processes may critically contribute to late graft loss. However, appropriate treatment for late AMR has not yet been defined. There is accumulating evidence that the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib may substantially affect the function and integrity of alloantibody-secreting plasma cells. The impact of this agent on the course of late AMR has not so far been systematically investigated.
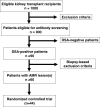
Methods/design: The BORTEJECT Study is a randomized controlled trial designed to clarify the impact of intravenous bortezomib on the course of late AMR. In this single-center study (nephrological outpatient service, Medical University Vienna) we plan an initial cross-sectional DSA screening of 1,000 kidney transplant recipients (functioning graft at ≥180 days; estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) >20 ml/minute/1.73 m2). DSA-positive recipients will be subjected to kidney allograft biopsy to detect morphological features consistent with AMR. Forty-four patients with biopsy-proven AMR will then be included in a double-blind placebo-controlled intervention trial (1:1 randomization stratified for eGFR and the presence of T-cell-mediated rejection). Patients in the active group will receive two cycles of bortezomib (4 × 1.3 mg/m2 over 2 weeks; 3-month interval between cycles). The primary end point will be the course of eGFR over 24 months (intention-to-treat analysis). The sample size was calculated according to the assumption of a 5 ml/minute/1.73 m2 difference in eGFR slope (per year) between the two groups (alpha: 0.05; power: 0.8). Secondary endpoints will be DSA levels, protein excretion, measured glomerular filtration rate, transplant and patient survival, and the development of acute and chronic morphological lesions in 24-month protocol biopsies.
Discussion: The impact of anti-humoral treatment on the course of late AMR has not yet been systematically investigated. Based on the hypothesis that proteasome inhibition improves the outcome of DSA-positive late AMR, we suggest that our trial has the potential to provide solid evidence towards the treatment of this type of rejection.
Trial registration: Clinicaltrials.gov: NCT01873157.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Late Antibody-Mediated Rejection in a Large Prospective Cross-Sectional Study of Kidney Allograft Recipients--Preliminary Results of the Screening Phase of the BORTEJECT Trial.Clin Transpl. 2014:189-95. Clin Transpl. 2014. PMID: 26281144 Clinical Trial.
-
Clazakizumab in late antibody-mediated rejection: study protocol of a randomized controlled pilot trial.Trials. 2019 Jan 11;20(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s13063-018-3158-6. Trials. 2019. PMID: 30635033 Free PMC article.
-
Bortezomib for refractory acute antibody-mediated rejection in kidney transplant recipients: A single-centre case series.Nephrology (Carlton). 2016 Aug;21(8):700-4. doi: 10.1111/nep.12659. Nephrology (Carlton). 2016. PMID: 26492594
-
The use of bortezomib as a rescue treatment for acute antibody-mediated rejection: report of three cases and review of literature.Transplant Proc. 2012 Dec;44(10):2971-5. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2012.02.037. Transplant Proc. 2012. PMID: 23195008 Review.
-
Proteasome inhibition with bortezomib: an effective therapy for severe antibody mediated rejection after renal transplantation.Clin Nephrol. 2012 Mar;77(3):246-53. doi: 10.5414/cn107156. Clin Nephrol. 2012. PMID: 22377258 Review.
Cited by
-
Rituximab in Combination With Bortezomib, Plasmapheresis, and High-Dose IVIG to Treat Antibody-Mediated Renal Allograft Rejection.Transplant Direct. 2016 Jul 1;2(8):e91. doi: 10.1097/TXD.0000000000000604. eCollection 2016 Aug. Transplant Direct. 2016. PMID: 27819032 Free PMC article.
-
Banff survey on antibody-mediated rejection clinical practices in kidney transplantation: Diagnostic misinterpretation has potential therapeutic implications.Am J Transplant. 2019 Jan;19(1):123-131. doi: 10.1111/ajt.14979. Epub 2018 Jul 19. Am J Transplant. 2019. PMID: 29935060 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in allograft vasculopathy.Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2017 Feb;22(1):1-7. doi: 10.1097/MOT.0000000000000370. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2017. PMID: 27898462 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Torque Teno Virus Load-Inverse Association With Antibody-Mediated Rejection After Kidney Transplantation.Transplantation. 2017 Feb;101(2):360-367. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000001455. Transplantation. 2017. PMID: 27525643 Free PMC article.
-
The Tao of myeloma.Blood. 2014 Sep 18;124(12):1873-9. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-05-578732. Blood. 2014. PMID: 25097176 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

