Characterization of small ruminant lentivirus A4 subtype isolates and assessment of their pathogenic potential in naturally infected goats
- PMID: 24708706
- PMCID: PMC3995504
- DOI: 10.1186/1743-422X-11-65
Characterization of small ruminant lentivirus A4 subtype isolates and assessment of their pathogenic potential in naturally infected goats
Abstract
Background: Small ruminant lentiviruses escaping efficient serological detection are still circulating in Swiss goats in spite of a long eradication campaign that essentially eliminated clinical cases of caprine arthritis encephalitis in the country. This strongly suggests that the circulating viruses are avirulent for goats.To test this hypothesis, we isolated circulating viruses from naturally infected animals and tested the in vitro and in vivo characteristics of these field isolates.
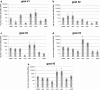
Methods: Viruses were isolated from primary macrophage cultures. The presence of lentiviruses in the culture supernatants was monitored by reverse transcriptase assay. Isolates were passaged in different cells and their cytopathogenic effects monitored by microscopy. Proviral load was quantified by real-time PCR using customized primer and probes. Statistical analysis comprised Analysis of Variance and Bonferroni Multiple Comparison Test.
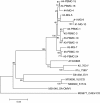
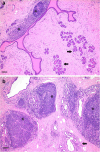
Results: The isolated viruses belonged to the small ruminant lentiviruses A4 subtype that appears to be prominent in Switzerland. The 4 isolates replicated very efficiently in macrophages, displaying heterogeneous phenotypes, with two isolates showing a pronounced cytopathogenicity for these cells. By contrast, all 4 isolates had a poor replication capacity in goat and sheep fibroblasts. The proviral loads in the peripheral blood and, in particular, in the mammary gland were surprisingly high compared to previous observations. Nevertheless, these viruses appear to be of low virulence for goats except for the mammary gland were histopathological changes were observed.
Conclusions: Small ruminant lentiviruses continue to circulate in Switzerland despite a long and expensive caprine arthritis encephalitis virus eradication campaign. We isolated 4 of these lentiviruses and confirmed their phylogenetic association with the prominent A4 subtype. The pathological and histopathological analysis of the infected animals supported the hypothesis that these A4 viruses are of low pathogenicity for goats, with, however, a caveat about the potentially detrimental effects on the mammary gland. Moreover, the high proviral load detected indicates that the immune system of the animals cannot control the infection and this, combined with the phenotypic plasticity observed in vitro, strongly argues in favour of a continuous and precise monitoring of these SRLV to avoid the risk of jeopardizing a long eradication campaign.
Figures



References
-
- Bertoni G, Blacklaws B. In: Lentiviruses and Macrophages: Molecular and Cellular Interactions. Desport M, editor. Norfolk, UK: Caister Academic Press; 2010. Small ruminant lentiviruses and cross-species transmission; pp. 277–306.
-
- Heaton MP, Clawson ML, Chitko-McKown CG, Leymaster KA, Smith TP, Harhay GP, White SN, Herrmann-Hoesing LM, Mousel MR, Lewis GS, Kalbfleisch TS, Keen JE, Laegreid WW. Reduced lentivirus susceptibility in sheep with TMEM154 mutations. PLoS Genet. 2012;8:e1002467. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002467. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- White SN, Mousel MR, Herrmann-Hoesing LM, Reynolds JO, Leymaster KA, Neibergs HL, Lewis GS, Knowles DP. Genome-wide association identifies multiple genomic regions associated with susceptibility to and control of ovine lentivirus. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e47829. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0047829. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Harmache A, Russo P, Vitu C, Guiguen F, Mornex JF, Pepin M, Vigne R, Suzan M. Replication in goats in vivo of caprine arthritis-encephalitis virus deleted in vif or tat genes: possible use of these deletion mutants as live vaccines. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1996;12:409–411. doi: 10.1089/aid.1996.12.409. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

