Plasma exchange successfully treats central pontine myelinolysis after acute hypernatremia from intravenous sodium bicarbonate therapy
- PMID: 24708786
- PMCID: PMC3986463
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2369-15-56
Plasma exchange successfully treats central pontine myelinolysis after acute hypernatremia from intravenous sodium bicarbonate therapy
Abstract
Background: Osmotic demyelination syndrome (ODS) primarily occurs after rapid correction of severe hyponatremia. There are no proven effective therapies for ODS, but we describe the first case showing the successful treatment of central pontine myelinolysis (CPM) by plasma exchange, which occurred after rapid development of hypernatremia from intravenous sodium bicarbonate therapy.
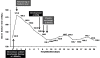
Case presentation: A 40-year-old woman presented with general weakness, hypokalemia, and metabolic acidosis. The patient was treated with oral and intravenous potassium chloride, along with intravenous sodium bicarbonate. Although her bicarbonate deficit was 365 mEq, we treated her with an overdose of intravenous sodium bicarbonate, 480 mEq for 24 hours, due to the severity of her acidemia and her altered mental status. The next day, she developed hypernatremia with serum sodium levels rising from 142.8 mEq/L to 172.8 mEq/L. Six days after developing hypernatremia, she exhibited tetraparesis, drooling, difficulty swallowing, and dysarthria, and a brain MRI revealed high signal intensity in the central pons with sparing of the peripheral portion, suggesting CPM. We diagnosed her with CPM associated with the rapid development of hypernatremia after intravenous sodium bicarbonate therapy and treated her with plasma exchange. After two consecutive plasma exchange sessions, her neurologic symptoms were markedly improved except for mild diplopia. After the plasma exchange sessions, we examined the patient to determine the reason for her symptoms upon presentation to the hospital. She had normal anion gap metabolic acidosis, low blood bicarbonate levels, a urine pH of 6.5, and a calyceal stone in her left kidney. We performed a sodium bicarbonate loading test and diagnosed distal renal tubular acidosis (RTA). We also found that she had Sjögren's syndrome after a positive screen for anti-Lo, anti-Ra, and after the results of Schirmer's test and a lower lip biopsy. She was discharged and treated as an outpatient with oral sodium bicarbonate and potassium chloride.
Conclusion: This case indicates that serum sodium concentrations should be carefully monitored in patients with distal RTA receiving intravenous sodium bicarbonate therapy. We should keep in mind that acute hypernatremia and CPM can be associated with intravenous sodium bicarbonate therapy, and that CPM due to acute hypernatremia may be effectively treated with plasma exchange.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[A case of central pontine myelinolysis and extrapontine myelinolysis during rapid correction of hypernatremia].Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 1994 Nov;34(11):1130-5. Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 1994. PMID: 7729094 Review. Japanese.
-
Topiramate-induced severe electrolyte abnormalities and hypernatremia leading to central pontine myelinolysis.BMJ Case Rep. 2021 Nov 30;14(11):e245870. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2021-245870. BMJ Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 34848414 Free PMC article.
-
Extrapontine myelinolysis associated with severe hypernatremia in infancy.Pediatr Int. 2016 Sep;58(9):936-9. doi: 10.1111/ped.13042. Epub 2016 Jul 27. Pediatr Int. 2016. PMID: 27463219
-
Diuretic abuse and central pontine myelinolysis.Psychother Psychosom. 1989;52(1-3):101-5. doi: 10.1159/000288307. Psychother Psychosom. 1989. PMID: 2486385
-
A novel association of osmotic demyelination in Sjögren's syndrome prompts revisiting role of aquaporins in CNS demyelinating diseases: A literature review.Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2023 Jan;69:104466. doi: 10.1016/j.msard.2022.104466. Epub 2022 Dec 11. Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2023. PMID: 36584554 Review.
Cited by
-
Atypical bromethalin intoxication in a dog: pathologic features and identification of an isomeric breakdown product.BMC Vet Res. 2015 Sep 28;11:244. doi: 10.1186/s12917-015-0554-y. BMC Vet Res. 2015. PMID: 26419228 Free PMC article.
-
Plasmapheresis for Extrapontine Myelinolysis: A Case Series and a Literature Review.Case Rep Neurol. 2022 Feb 15;14(1):72-81. doi: 10.1159/000521814. eCollection 2022 Jan-Apr. Case Rep Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35350290 Free PMC article.
-
A rare presentation of central pontine myelinolysis secondary to hyperglycaemia.BMC Endocr Disord. 2023 May 10;23(1):106. doi: 10.1186/s12902-023-01361-y. BMC Endocr Disord. 2023. PMID: 37165361 Free PMC article.
-
Delayed Presentation of Osmotic Demyelination Syndrome Treated With Plasmapheresis.Cureus. 2023 Oct 20;15(10):e47399. doi: 10.7759/cureus.47399. eCollection 2023 Oct. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 38021548 Free PMC article.
-
How Dangerous Is Hyperkalemia?J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017 Nov;28(11):3155-3165. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2016121344. Epub 2017 Aug 4. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 28778861 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sterns RH, Cappuccio JD, Silver SM, Cohen EP. Neurologic sequelae after treatment of severe hyponatremia: a multicenter perspective. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1994;4:1522–1530. - PubMed
-
- Go M, Amino A, Shindo K, Tsunoda S, Shiozawa Z. A case of central pontine myelinolysis and extrapontine myelinolysis during rapid correction of hypernatremia. Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 1994;34:1130–1135. - PubMed
-
- Bibl D, Lampl C, Gabriel C, Jungling G, Brock H, Kostler G. Treatment of central pontine myelinolysis with therapeutic plasmapheresis. Lancet. 1999;353:1155. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous