Randomized controlled trial to evaluate the effects of combined progressive exercise on metabolic syndrome in breast cancer survivors: rationale, design, and methods
- PMID: 24708832
- PMCID: PMC3985576
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-238
Randomized controlled trial to evaluate the effects of combined progressive exercise on metabolic syndrome in breast cancer survivors: rationale, design, and methods
Abstract
Background: Metabolic syndrome (MetS) is increasingly present in breast cancer survivors, possibly worsened by cancer-related treatments, such as chemotherapy. MetS greatly increases risk of cardiovascular disease and diabetes, co-morbidities that could impair the survivorship experience, and possibly lead to cancer recurrence. Exercise has been shown to positively influence quality of life (QOL), physical function, muscular strength and endurance, reduce fatigue, and improve emotional well-being; however, the impact on MetS components (visceral adiposity, hyperglycemia, low serum high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, hypertriglyceridemia, and hypertension) remains largely unknown. In this trial, we aim to assess the effects of combined (aerobic and resistance) exercise on components of MetS, as well as on physical fitness and QOL, in breast cancer survivors soon after completing cancer-related treatments.
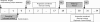
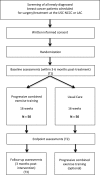
Methods/design: This study is a prospective randomized controlled trial (RCT) investigating the effects of a 16-week supervised progressive aerobic and resistance exercise training intervention on MetS in 100 breast cancer survivors. Main inclusion criteria are histologically-confirmed breast cancer stage I-III, completion of chemotherapy and/or radiation within 6 months prior to initiation of the study, sedentary, and free from musculoskeletal disorders. The primary endpoint is MetS; secondary endpoints include: muscle strength, shoulder function, cardiorespiratory fitness, body composition, bone mineral density, and QOL. Participants randomized to the Exercise group participate in 3 supervised weekly exercise sessions for 16 weeks. Participants randomized to the Control group are offered the same intervention after the 16-week period of observation.
Discussion: This is the one of few RCTs examining the effects of exercise on MetS in breast cancer survivors. Results will contribute a better understanding of metabolic disease-related effects of resistance and aerobic exercise training and inform intervention programs that will optimally improve physiological and psychosocial health during cancer survivorship, and that are ultimately aimed at improving prognosis.
Trial registration: NCT01140282;
Registration: June 10, 2010.
Figures
References
-
- Ries L, Melbert D, Krapcho M, Mariotto A, Miller BA, Feuer EJ, Clegg L, Horner MJ, Howlader N, Eisner MP, Reichman M, Edwards BK, editor. SEER Cancer Statistics review, 1975–2004. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute; 2006.
-
- Irwin ML, Crumley D, McTiernan A, Bernstein L, Baumgartner R, Gilliland FD, Kriska A, Ballard-Barbash R. Physical activity levels before and after a diagnosis of breast carcinoma: the health, eating, activity, and lifestyle (HEAL) study. Cancer. 2003;97(7):1746–1757. doi: 10.1002/cncr.11227. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Irwin ML, Smith AW, McTiernan A, Ballard-Barbash R, Cronin K, Gilliland FD, Baumgartner RN, Baumgartner KB, Bernstein L. Influence of pre- and postdiagnosis physical activity on mortality in breast cancer survivors: the health, eating, activity, and lifestyle study. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(24):3958–3964. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2007.15.9822. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical