Catheter-based radiorefrequency renal denervation lowers blood pressure in obese hypertensive dogs
- PMID: 24709437
- PMCID: PMC4184388
- DOI: 10.1093/ajh/hpu048
Catheter-based radiorefrequency renal denervation lowers blood pressure in obese hypertensive dogs
Erratum in
-
Erratum.Am J Hypertens. 2015 Jan;28(1):146. doi: 10.1093/ajh/hpu232. Epub 2014 Nov 13. Am J Hypertens. 2015. PMID: 25395612 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Obesity-induced hypertension appears to be due, in part, to increased renal sympathetic activity. Catheter-based renal denervation (RD) has been reported to lower arterial blood pressure (BP) in humans with resistant hypertension, many of whom are obese. This study was performed to assess the impact of radiofrequency-induced RD on renal function, BP, renal norepinephrine (NE), and histology of nerves along the renal artery in obese, hypertensive dogs, an experimental model that closely mimics cardiorenal and metabolic changes in obese hypertensive humans.
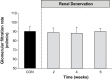
Methods: After control measurements of cardiovascular and renal function were obtained in obese dogs fed a high-fat diet, bilateral RD was performed using the St. Jude Medical EnligHTN RD system. After RD, BP was measured continuously for 8 weeks, and glomerular filtration rate (GFR) was measured biweekly for 6 weeks. At the end of the study, renal arteries were collected for histological analysis, and kidneys were obtained for NE measurement.
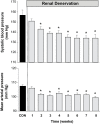
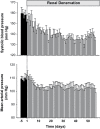
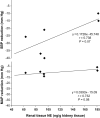
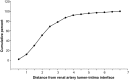
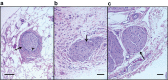
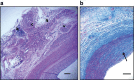
Results: Eight weeks after RD, systolic BP fell from 157 ± 5 mm Hg pre-RD to 133 ± 3 mm Hg (P < 0.01), and mean arterial pressure decreased by 9 mm Hg compared with pre-RD (P < 0.01). There were no significant changes in GFR. Renal nerve injury was most prevalent 0.28-3.5mm from the renal artery lumen. RD caused injury in 46% of the renal nerves observed and reduced renal tissue NE by 42% (P < 0.01).
Conclusions: Catheter-based RD with the St. Jude Medical EnligHTN system lowers BP in obese dogs without significantly compromising renal function.
Keywords: blood pressure; glomerular filtration; hypertension; obesity; renal denervation..
© American Journal of Hypertension, Ltd 2014. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
Comment in
-
Renal nerves: time for reassessment of their role in hypertension?Am J Hypertens. 2014 Oct;27(10):1245-7. doi: 10.1093/ajh/hpu096. Epub 2014 May 28. Am J Hypertens. 2014. PMID: 24871630 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Kearney PM, Whelton M, Reynolds K, Muntner P, Whelton PK, He J. Global burden of hypertension: analysis of worldwide data. Lancet 2005; 365:217––223. - PubMed
-
- Mancia G, De Backer G, Dominiczak A, Cifkova R, Fagard R, Germano G, Grassi G, Heagerty AM, Kjeldsen SE, Laurent S, Narkiewicz K, Ruilope L, Rynkiewicz A, Schmieder RE, Boudier HA, Zanchetti A, Vahanian A, Camm J, De Caterina R, Dean V, Dickstein K, Filippatos G, Funck-Brentano C, Hellemans I, Kristensen SD, McGregor K, Sechtem U, Silber S, Tendera M, Widimsky P, Zamorano JL, Erdine S, Kiowski W, Agabiti-Rosei E, Ambrosioni E, Lindholm LH, Viigimaa M, Adamopoulos S, Bertomeu V, Clement D, Farsang C, Gaita D, Lip G, Mallion JM, Manolis AJ, Nilsson PM, O’Brien E, Ponikowski P, Redon J, Ruschitzka F, Tamargo J, van Zwieten P, Waeber B, Williams B. Management of Arterial Hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension, European Society of Cardiology. 2007 Guidelines for the Management of Arterial Hypertension: fhe Task Force for the Management of Arterial Hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). J Hypertens 2007; 25:1105––1187. - PubMed
-
- Schlaich MP, Schmieder RE, Bakris G, Blankestijn PJ, Böhm M, Campese VM, Francis DP, Grassi G, Hering D, Katholi R, Kjeldsen S, Krum H, Mahfoud F, Mancia G, Messerli FH, Narkiewicz K, Parati G, Rocha-Singh KJ, Ruilope LM, Rump LC, Sica DA, Sobotka PA, Tsioufis C, Vonend O, Weber MA, Williams B, Zeller T, Esler MD. International expert consensus statement: percutaneous transluminal renal denervation for the treatment of resistant hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol 2013; 62:2031–2045. - PubMed
-
- Garrison RJ, Kannel WB, Stokes J, 3rd, Castelli WP. Incidence and precursors of hypertension in young adults: the Framingham Offspring Study. Prev Med 1987; 16:235––251. - PubMed
-
- Hall JE, Brands MW, Dixon WN, Smith MJ., Jr Obesity-induced hypertension. Renal function and systemic hemodynamics. Hypertension 1993; 22:292––299. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

