The anti-apoptotic role of neurotensin
- PMID: 24709648
- PMCID: PMC3972661
- DOI: 10.3390/cells2010124
The anti-apoptotic role of neurotensin
Abstract
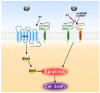
The neuropeptide, neurotensin, exerts numerous biological functions, including an efficient anti-apoptotic role, both in the central nervous system and in the periphery. This review summarizes studies that clearly evidenced the protective effect of neurotensin through its three known receptors. The pivotal involvement of the neurotensin receptor-3, also called sortilin, in the molecular mechanisms of the anti-apoptotic action of neurotensin has been analyzed in neuronal cell death, in cancer cell growth and in pancreatic beta cell protection. The relationships between the anti-apoptotic role of neurotensin and important physiological and pathological contexts are discussed in this review.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources