Flotillins in receptor tyrosine kinase signaling and cancer
- PMID: 24709906
- PMCID: PMC3980747
- DOI: 10.3390/cells3010129
Flotillins in receptor tyrosine kinase signaling and cancer
Abstract
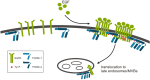
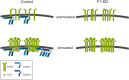
Flotillins are highly conserved proteins that localize into specific cholesterol rich microdomains in cellular membranes. They have been shown to be associated with, for example, various signaling pathways, cell adhesion, membrane trafficking and axonal growth. Recent findings have revealed that flotillins are frequently overexpressed in various types of human cancers. We here review the suggested functions of flotillins during receptor tyrosine kinase signaling and in cancer. Although flotillins have been implicated as putative cancer therapy targets, we here show that great caution is required since flotillin ablation may result in effects that increase instead of decrease the activity of specific signaling pathways. On the other hand, as flotillin overexpression appears to be related with metastasis formation in certain cancers, we also discuss the implications of these findings for future therapy aspects.
Figures
References
-
- Kurrle N., John B., Meister M., Tikkanen R. Function of Flotillins in Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Signaling and Endocytosis: Role of Tyrosine Phosphorylation and Oligomerization. In: Huang C., editor. Protein Phosphorylation in Human Health. InTech Publisher; Rijeka, Croatia: 2012.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

